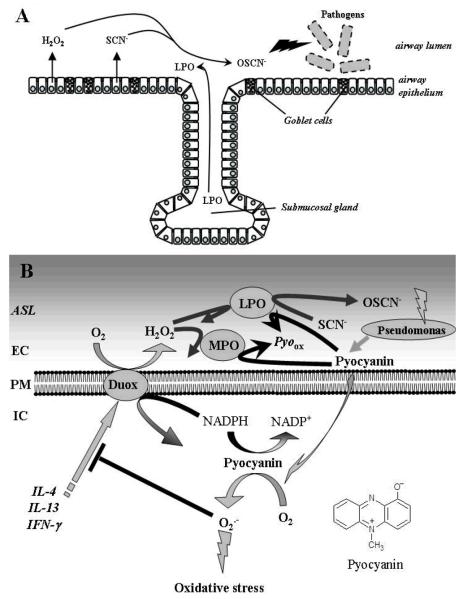
Fig.1. The oxidative antimicrobial Duox/SCN-/LPO-system of major airways and counteroffensive mechanisms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa imposed by the redox active virulence factor pyocyanin.
A) Lactopreoxidase is produced in the submucosal glands of the airways and accumulates in the airway surface layer, where it converts thiocyanate into microbicidal hypothiocanite using Duox-derived hydrogen peroxide. B) The redox-active Pseudomonas pigment, pyocyanin, enters airway cells, inhibits Duox activity by competing for its substrate (NADPH), and by inhibiting Duox expression. The airway peroxidases, lactoperoxidase (LPO) and myeloperoxidase (MPO), can detoxify pyocyanin using Duox-derived hydrogen peroxide. (Adapted from refs. 7 and 47)