Figure 4. Caveolin-1 phosphorylation mediates H2O2-induced dissociation of caveolin-1 from β-catenin.
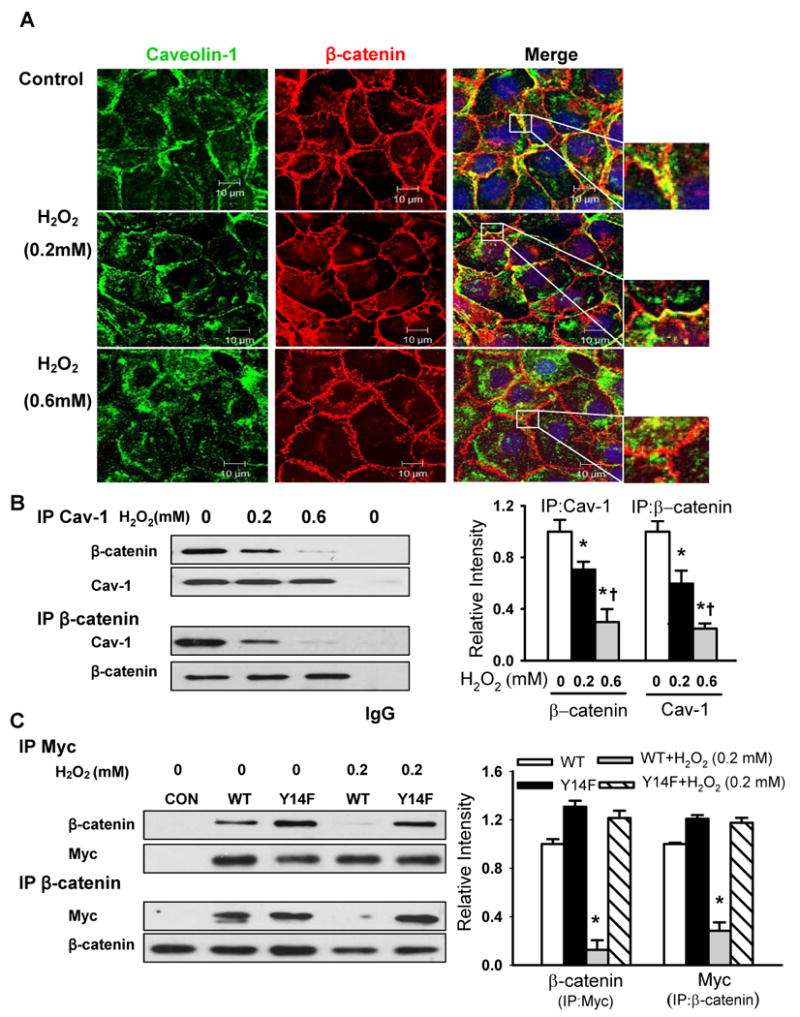
(A) Effects of H2O2 on the co-localization of caveolin-1 (green) and β-catenin (red) in naïve RLMVECs. Cells were exposed to different concentrations of H2O2 for 30 min. The nucleus (blue) was stained with DAPI. Scale bars =10 μm. (B, C) The association of endogenous caveolin-1 (B) or over-expressed Myc-tagged WT-Cav-1 or Y14F-Cav-1 mutant (C) with β-catenin in naïve endothelial cells and stable endothelial cell lines was determined by immunoprecipitation and immunoblot (IP/IB) with anti-caveolin-1, anti-Myc, or anti-β-catenin antibodies. Left, representative Western blots for β-catenin and caveolin-1 (or Myc); Right, protein quantification by densitometry. The density of proteins in each untreated control group was used as a standard (1 arbitrary unit) to compare the relative density of the other groups. *P < 0.05 compared to control (untreated) groups; † P < 0.05 compared with H2O2 (0.2 mmol/L) groups.
