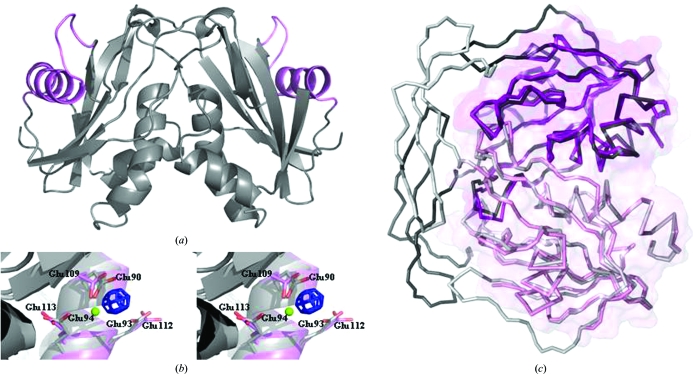
Figure 2.
(a) The overall structure of the DR2204 dimer as observed in the asymmetric unit. The protein in grey is shown in cartoon representation, with the Nudix box highlighted in magenta. (b) Stereo picture showing a close-up of the Nudix box. The experimental map (blue; contoured at 10.0σ) calculated from data collected from the gadolinium-derivative crystal used for phasing is overlaid on the final model refined from data collected from the native crystal (magenta). A significant positive peak for the Gd3+ ion is observed in the region where Mg2+ is expected to bind during catalysis, between the side chains of Glu109 and Glu112. Both residues are located in the Nudix-box region, a versatile divalent metal-binding site characteristic of this family of enzymes. For clarity, the model of the ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase (Ndx2) from T. thermophilus (grey; PDB code 2yvm) including the Mg2+ 1002 ion (in green) bound to residues Glu90 and Glu94 is shown. (c) Superposition of DR2204 (magenta) on the structures of the ADP-ribose pyrophosphatase from T. thermophilus (grey; 0.73 Å r.m.s.d.; PDB code 2yvm). The surface of DR2204 is overlaid on the proteins represented in ribbon; the dimer formation buries ∼1100 Å2 of solvent-accessible surface. This figure was prepared with PyMOL (DeLano, 2003 ▶).