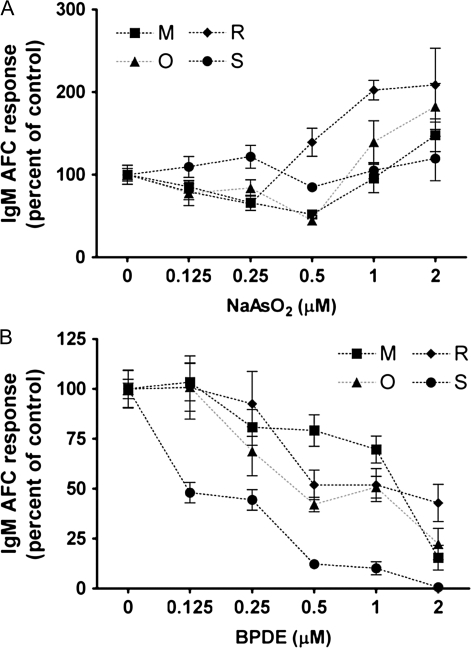
FIG. 9.
Effect of arsenic and BPDE on the CD40L-induced IgM AFC response from human B cells. Human CD19+CD27− naive B cells (1.5 × 105 cell/culture) were treated with (A) NaAsO2 or (B) BPDE at indicated concentrations or VH and then cocultured with irradiated CD40L-L cells (1.5 × 103 cell/culture) in the presence of recombinant human IL-2, IL-6, and IL-10 for 4 days and further cultured for additional 3 days without CD40L-L cells. Cells were harvested on day 7 to enumerate IgM-secreting cells by ELISPOT. The cell number was determined using a particle counter, and the viability was assessed by a pronase activity assay. Data were normalized to the VH-treated group (100%) and presented as percent of control with six replicates per group. B cells from four human donors were assessed. The IgM AFC responses of B cells derived from two donors were not modulated by either arsenic or BPDE at all concentrations tested and cells demonstrated a highly proliferative phenotype. Data from these two donors were not included in this figure. The error bars indicate SE calculated for replicates of each treatment group.