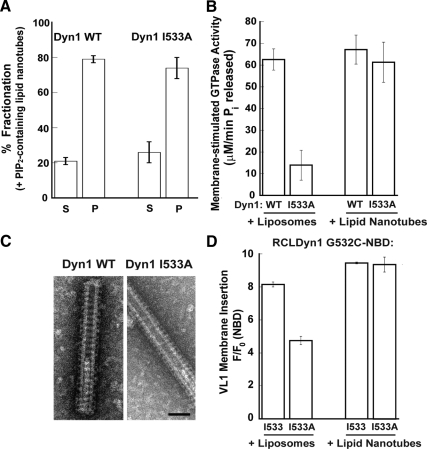
Figure 5.
Precurved lipid templates rescue Dyn1 I533A. (A) Sedimentation analysis of 1.0 μM Dyn1 I533A on preformed PIP2-containing lipid nanotubes (300 μM total lipid) was performed and plotted as in Figure 1C. (B) Assembly-stimulated GTP hydrolysis rate of 0.5 μM Dyn1 WT or Dyn1 I533A induced upon preincubation with either PIP2-containing liposomes or PIP2-containing lipid nanotubes (150 μM total lipid) is plotted as μM Pi released per minute. (C) Representative electron micrographs of Dyn1 WT and Dyn1 I533A self-assembled on PIP2-containing lipid nanotubes. Scale bar, 50 nm. (D) The magnitude of VL1-membrane binding in 0.1 μM RCLDyn1 (G532C-NBD), I533 or I533A, was determined by detecting the fold increase in the steady-state emission intensity of NBD upon incubation with either PIP2-containing liposomes or PIP2-containing lipid nanotubes (30 μM total lipid). F/F0 is the ratio of the emission intensity values obtained for NBD before (F0) and after (F) incubation with the corresponding lipid templates.