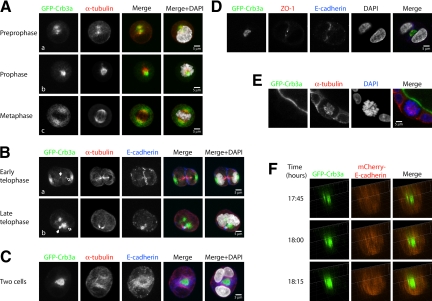
Figure 2.
Lumen formation occurs during the first cell division of ECM-embedded MDCKII cells through positioning of apical membrane in the plane of division. (A–C) GFP-Crb3a–expressing (green) MDCKII cells were grown as single-cell suspensions in Geltrex-containing medium and were fixed at 12 h (for mitotic stages) or 24 h (for two-cell stages) after embedding. Cells were stained for E-cadherin (blue), α-tubulin (red), and DAPI (gray) and analyzed by confocal laser microscopy. (A, collapsed Z-stacks) During early stages of cell division GFP-Crb3a localizes to cytosolic compartments located around the mitotic spindle apparatus and partitions to both sides of the condensing nucleus during metaphase. (B, collapsed Z-stacks) At later mitotic stages, it relocates from a position at the lateral side of the nucleus (subpanel a) to the medial side of the two new daughter nuclei (outlined arrows) and finally forms a nascent lumen in the plane of the cell adhesion at the two-cell stage (C, collapsed Z-stacks). Note that GFP-Crb3a is evident at the tips of the midzone microtubule bundles (B, subpanels a and b, white arrows). (D) Single Z-section of a GFP-Crb3a–expressing two-cell stage, costained against ZO-1 (red) and DAPI (gray). (E, single Z-section) GFP-Crb3a only locates to spindle poles during early but not late cell divisions. GFP-Crb3a–expressing MDCKII cells in Geltrex-containing medium grown from single-cell suspensions were fixed after 8 d and stained for α-tubulin (red) and DAPI (blue). (F) Live-cell imaging of lumen formation during MDCKII cell division. MDCKII cells were sequentially virally transduced with GFP-Crb3a (in pRevTRE) and mCherry-E-cadherin (in pQCXIP). Images were three-dimensionally reconstructed at individual time points. The adhering membranes between two-daughter cells are displayed in side view, showing an emerging Crb3a-positive apical lumen.