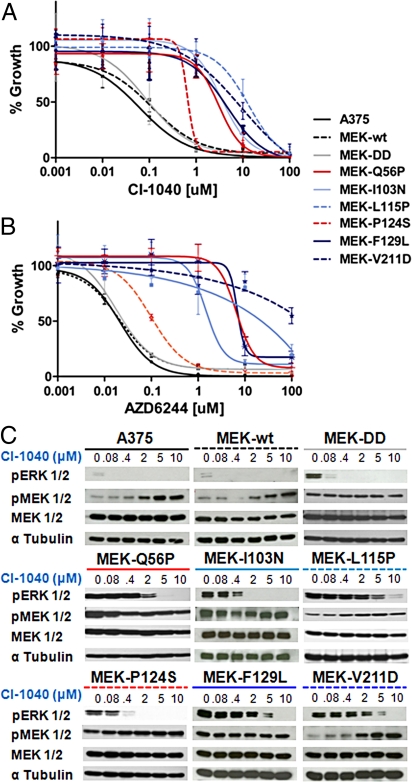
Fig. 2.
Functional characterization of MEK1 resistance mutations identified in vitro. Growth inhibition curves of parental A375 (solid black), A375 cells expressing primary or secondary MEK1 resistance alleles, a constitutive active MEK variant (MEK-DD; grey), or wild-type MEK1 (hatched black) are shown for CI-1040 (A) or AZD6244 (B). (C) The levels of pERK1/2, pMEK1/2, MEK1/2, and α-tubulin are shown for A375 cells expressing MEK1 mutations following 16-hour incubation with CI-1040 at 10 μM, 5 μM, 2 μM, 0.4 μM, 0.08 μM, and 0 μM.