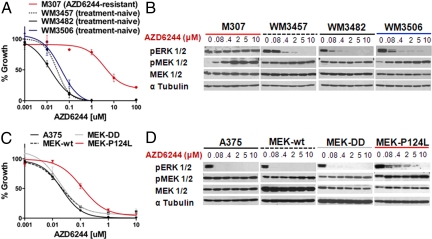
Fig. 4.
Ex vivo and functional characterization of MEK1(P124L). (A) AZD6244-mediated growth inhibition ex vivo of treatment-naïve BRAFV600E melanoma cells (black and blue) or cells cultured from an AZD6244-resistant metastatic focus (red). (B) ERK phosphorylation (p-ERK) and MEK phosphorylation (p-MEK) are shown following treatment with increasing concentrations of AZD6244 in treatment-naïve or AZD6244-resistant melanoma cells cultured ex vivo. The tubulin loading control (α-tubulin) is also shown. (C) AZD6244 growth inhibition curves of parental A375 (solid black), A375 cells expressing MEK-DD (grey), wild-type MEK1 (hatched black), or MEK1(P124L) (red) are shown. In each instance n = 6 and ± error = standard deviation. (D) p-ERK and p-MEK are shown following treatment with increasing AZD6244 concentrations in the cell lines described in C, Above. The α-tubulin control is also shown.