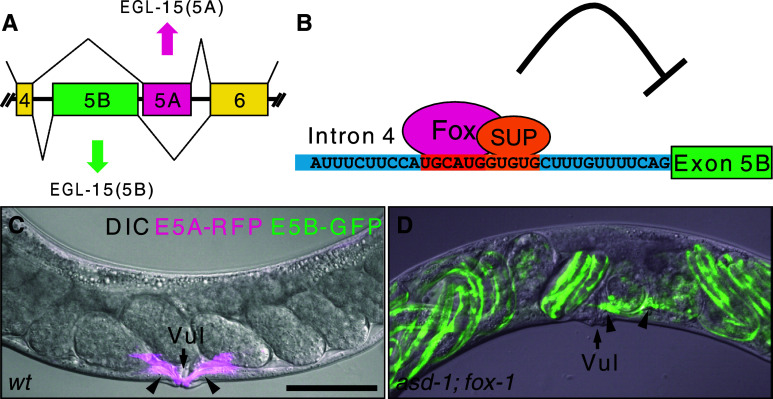
Fig. 5.
Fox-1 family proteins ASD-1 and FOX-1 regulate tissue-specific mutually exclusive alternative splicing of the FGFR gene, egl-15, in C. elegans. a Tissue-specific mutually exclusive selection exons of the egl-15 gene of C. elegans. Note that muscle-specific exon 5A resides downstream of exon 5B. b Schematic illustration of muscle-specific repression of exon 5B. Nucleotide sequence of the UIF region is presented. The cis-elements for tissue-specific regulation are in orange. Fox, ASD-1 or FOX-1; SUP, SUP-12. (c,d) Left lateral view of adult hermaphrodite worms expressing egl-15 alternative splicing reporter in body wall muscles and vulval muscles in the wild-type (wt) background (c) and the asd-1; fox-1 double mutant background (d). Merged images of DIC and confocal images of GFP (green) and RFP (magenta). The egl-15 alternative splicing reporter worms express either RFP, representing exon 5A selection, or GFP, representing exon 5B selection, in body wall muscles and vulval muscles (see [16] for detail). Note that in the asd-1; fox-1 double mutant, vulval muscles (arrowheads) express GFP and are mislocalized off the vulva (Vul, arrows), and late embryos with reporter expression in body wall muscles retained in the uterus. Anterior is to the left. Scale bar in (c) 50 μm. (c,d) are modified from [16]