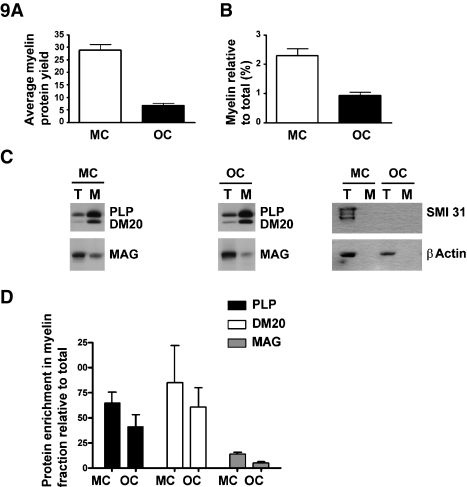
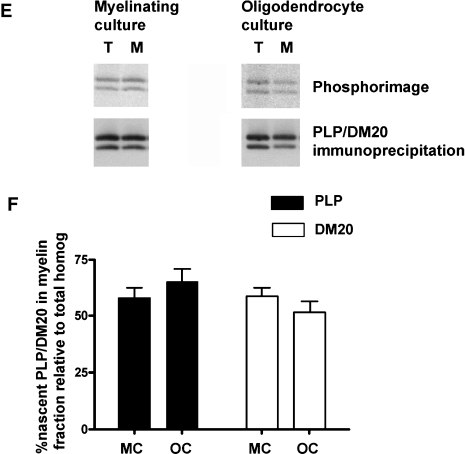
Fig. 9.
Myelin-enriched fraction can be isolated from myelinating cultures and used for myelin protein kinetic studies. (A) The data shown indicate the average protein yield (28.9 ± 2.2 μg) of the myelin fraction obtained from three experimental repeats for myelinating cultures (MC) as compared with the yield (6.7 ± 0.9 μg) from the myelin-like fraction isolated from oligodendrocyte cultures (OC). Each preparation was from one litter of five to seven embryos or five or six pups. Each tissue source yielded sufficient material to generate 6 × 35-mm2 Petri dish cultures. (B) The average protein recovered from the myelin fraction for each preparation is expressed relative to the total protein content of the homogenate. (C) Representative examples of western blot analysis of the two myelin proteins proteolipid protein (PLP)–DM20 and myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) detected in the total homogenate and myelin fraction from each culture type. The total homogenate (T) and the myelin fractions (M) were loaded onto the gel at a ratio of 20 : 1 (typically 20 μg and 1 μg respectively). Western blot staining for neuronal proteins (phosphorylated neurofilament) showed that there was no detectable contamination of the myelin fraction harvested from the myelinating cultures. It also showed that a significant proportion of the protein in the total cell homogenate of myelinating cultures is neuronally derived. The blots were stripped and reprobed with β-actin to assess equivalence of loading. (D) The intensity of the protein in the myelin fraction was corrected for the amount loaded onto the gel and expressed as the fold enrichment relative to the total homogenate intensity. (E) Nascent PLP and DM20 isoforms were incorporated into the myelin fraction. Representative phosphorimages of nascent PLP and DM20 immunoprecipitated from the myelin fraction and total homogenate are shown for each culture type. The nitrocellulose membranes were analysed by western blotting to compare the levels of PLP and DM20 isoforms recovered from each fraction. (F) The western blots were then quantitatively analysed by assessing the intensity of the signal for nascent PLP and DM20 isoforms relative to the total cellular homogenate. Note that the quantification is of the actual signal intensities in these blots, which were derived from loading 20 times more total cell homogenate then myelin fraction. Thus, if this 20-fold factor is taken into account, the absolute yield of PLP and DM20 in the myelin fraction is much higher than in the total cell homogenate.