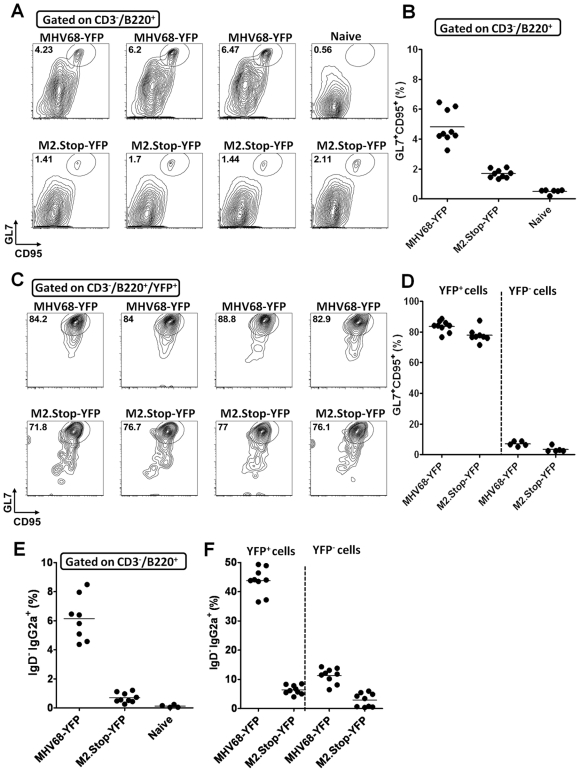
Figure 3. M2 null virus infected B cells form germinal centers, but exhibit a defect in immunoglobulin isotype class switching.
Mice were infected with a 100 pfu of either MHV68-YFP or M2.Stop-YFP viruses via intranasal inoculation. (A) Total germinal center B cells (CD3−/B220+/GL7hi/CD95hi) present in the spleen are reduced in M2.stop-YFP infected mice compared to MHV68-YFP infected mice at day 16. Representative flow cytometry plots are shown for 3–4 individual mice. (B) Scatter plot depicting the percentage of total B220+ splenocytes that are germinal center B cells (GL7+/CD95+) in naïve mice, MHV68-YFP or M2stop-YFP infected spleens at day 16 post-infection. (C) The distribution of wild type and M2 null virus infected B cells (YFP+ cells) in the spleens of infected mice. (D) Percentage of wild type and M2 null virus infected (YFP+) B cells vs uninfected B cells (YFP-) in the spleen that exhibited a germinal center phenotype. (E) Percentage of splenic B cells that were IgG2a+ in wild type vs M2 null virus infected mice at day 16 post-infection. (F) M2.stop-YFP+ spleen cells showed an impaired ability to class-switch to IgG2a.