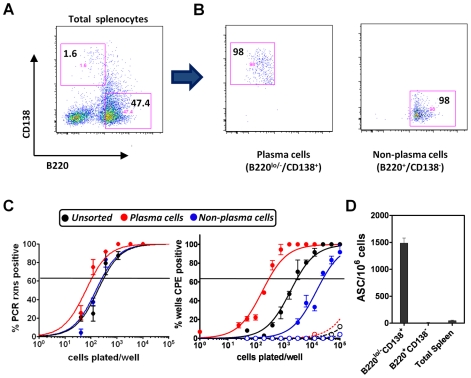
Figure 5. Plasma cells contribute significantly to spontaneous MHV68 reactivation following explant.
(A and B) Purification of plasma cells and non-plasma cells by flow cytometry. Shown are representative flow plots unsorted (A) and post-sorting (B), as well as the gates used to isolate the plasma cells and non-plasma cell populations. Cells were sorted from MHV68-YFP infected spleens at day 16 post-infection. (C) Limiting dilution determinations of the frequency of splenocyte populations harboring the MHV68 genome (left panel) or spontaneously reactivating virus upon explant (right panel). Splenocytes were harvested from C57Bl/6 mice at day 16 post-infection. For the reactivation analyses, both intact cells (filled symbols) and mechanically disrupted cells (open symbols) were plated to distinguish the presence of pre-formed infectious virus from reactivating virus. (D) ELISPOT analyses of antibody secreting cells in the unsorted and purified plasma cell and non-plasma cell populations analyzed in (A).