Fig. 1.
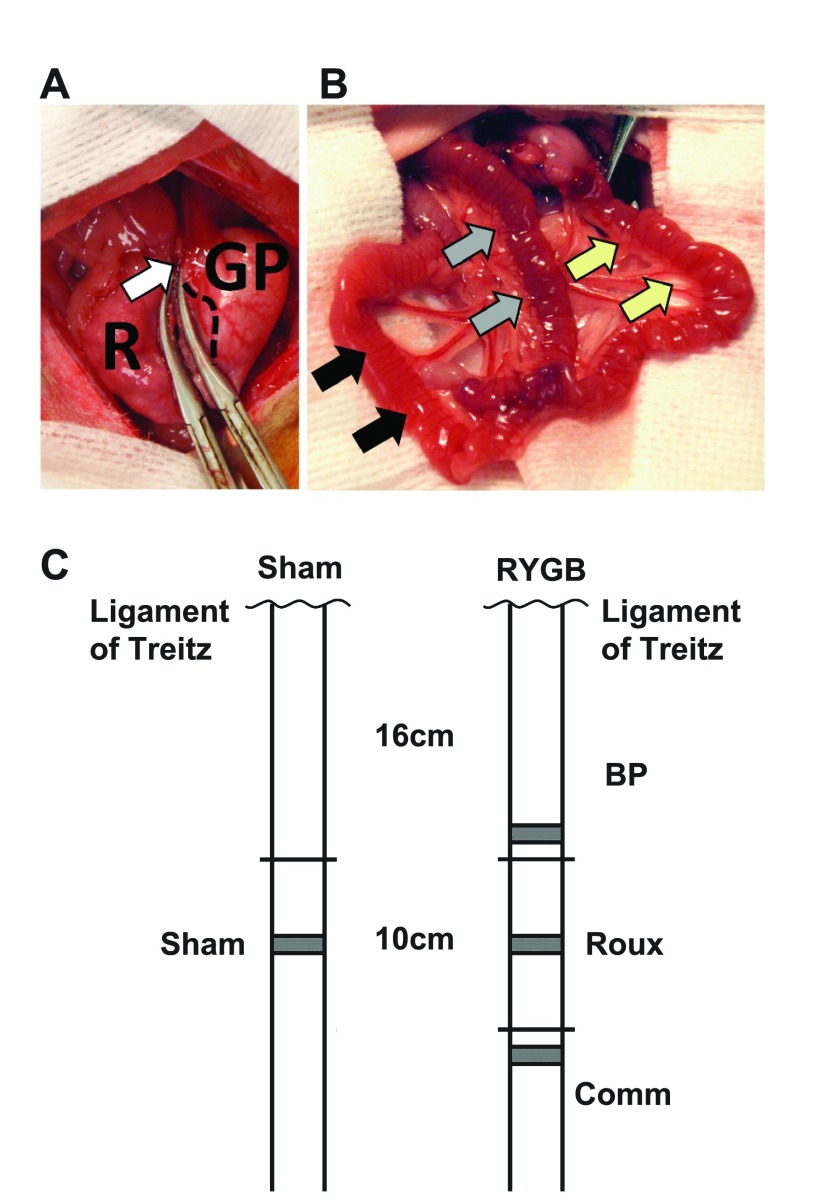
A: Transection of the stomach between hemostats, with the gastric pouch (GP) and gastric remnant (R). The gastric pouch includes glandular mucosa, with the junction between the glandular and squamous mucosa indicated with a dashed line. The vagus has been mobilized and preserved along with the left and right gastric vessels in the lesser curve (white arrow). B: final reconstruction, with a 10-cm Roux limb (yellow arrows) draining the gastric pouch before continuing as the common channel (black arrows). The Roux limb is joined by the 16-cm biliopancreatic (BP) limb, identified with gray arrows. C: schematic diagram showing the orthotopic position of BP, Roux, and common (Comm) limbs compared with the ligament of Trietz, and compared with sham animals. Sections for histology were taken from the gray shaded regions: these were all less than 8 cm from the orthotopic position of the sham jejunum.