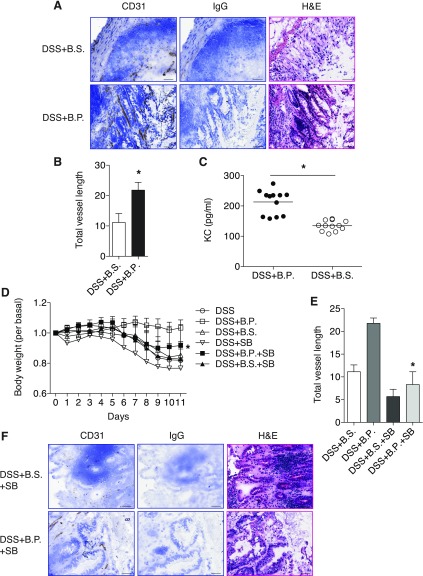
Fig. 5.
B.P. increases angiogenesis during wound healing. Mice were supplied with 4% DSS in drinking water for 7 days followed by 1% DSS for 4 days. One group of mice was supplied with B.P. and the other group of mice was supplied with B.S. via oral gavage. Tissues were collected and embedded for frozen sections. A: immunohistochemistry for CD31 was performed in both B.P.-treated and B.S.-treated groups by using sections. Tissues from the mice with B.P. treatment showed increased CD31 staining compared with B.S.-treated mice, suggesting increased angiogenesis. Rat IgG2a control was used instead of antibody as a negative control. Bar, 50 μm. B: total vessel length was measured by use of the Image J program. The B.P.-treated group showed increased total vessel length compared with B.S.-treated mice. Data are shown as means ± SD; n = 5 per group; *P < 0.01 vs. DSS+B.S. C: the result of ELISA for KC indicated that mice fed with B.P. showed increased KC production compared with B.S.-treated mice. n = 12; *P < 0.01 vs. DSS+B.S. D: mice treated with B.P. plus SB showed increased body weight compared with B.P. alone-treated mice. Data are shown as means ± SD; n = 4–7 per group; *P < 0.01 vs. DSS+B.P. E: total vessel length was measured with the Image J program. B.P. plus SB-treated group showed reduced total vessel length compared with B.P. alone-treated mice. Data are shown as means ± SD; n = 3–5 per group; *P < 0.001 vs. DSS+B.P. F: immunohistochemistry for CD31 was performed. Tissues from the mice with B.P. plus SB treatment showed reduced CD31 staining compared with B.P. alone-treated mice (A). Rat IgG2a control was used instead of the CD31 antibody as a negative control. Bar, 50 μm.