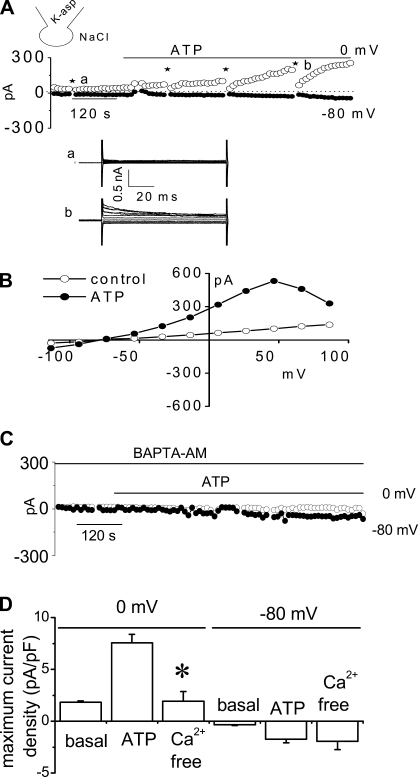
Fig. 2.
Characterization of whole cell ATP stimulated outward currents. Exposure to ATP stimulates outward currents in human Mz-Cha-1 biliary epithelial cells when intracellular KCl was replaced with K-aspartate (methods). Whole cell currents were measured during basal conditions and during exposure to ATP (50 μM) (methods). A: representative whole cell recording. Currents measured at 0 mV (○), representing IK+, and at −80 mV (●), representing ICl−, are shown. ATP exposure is indicated by the bar. A voltage-step protocol (test potentials between −100 mV and +100 mV in 20-mV increments) was obtained at a★ (basal) and b★ (maximal current response) as indicated. The I-V plot shown in 2B was generated from these protocols. B: I-V relationship of whole cell currents during basal (○) and ATP-stimulated (●) conditions. C: representative ATP-stimulated whole cell current tracings measured at 0 and −80 mV in the absence of intracellular Ca2+ (pretreated with BAPTA-AM 50 μM for 5–10 min and EGTA 2 mM in pipette solution). D: cumulative data demonstrating magnitude of ATP-stimulated currents in control conditions or after removal of intracellular Ca2+ (pretreated with BAPTA-AM 50 μM for 5–10 min and EGTA 2 mM in pipette solution). Values represent maximum current density measured at 0 and −80 mV (n = 3–10 each). *ATP-stimulated currents were significantly inhibited (P < 0.05 for each).