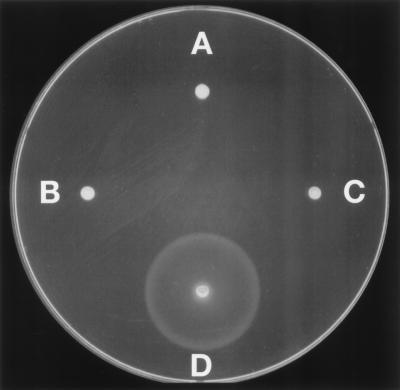
Figure 1.
Complementation of the fliG motA double-mutant strain by wild-type fliG and motA genes on plasmids. Shown are swarms in soft-agar plates of (A) strain DFB245, a fliG motA double mutant; (B) strain DFB245 transformed with plasmid pSL27, which encodes FliG; (C) strain DFB245 transformed with plasmid pJZ19, which encodes MotA; and (D) strain DFB245 transformed with both pSL27 and PJZ19. Flagellar staining showed that strains A and C were nonflagellate, whereas strains B and D had 2.4 and 4.5 flagella per cell, respectively (averages for 50 cells).