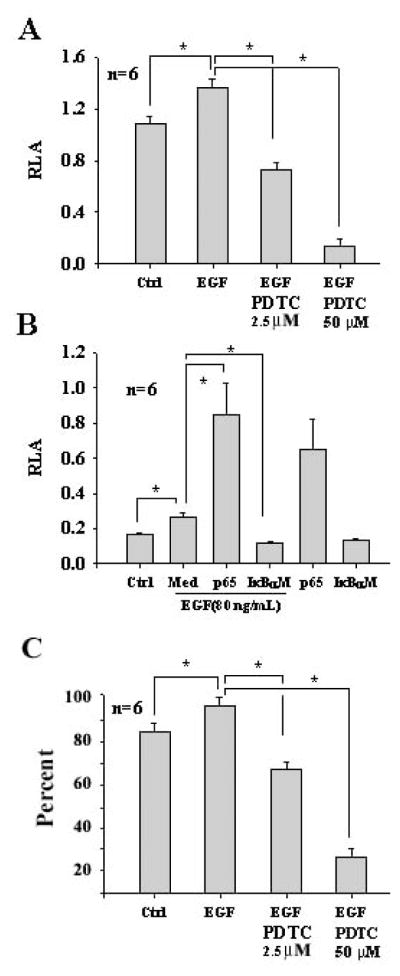
Fig. 3.
Increase of the NF-κB promoter activity and cell survival by EGF in OC1 cells. Incubation of OC1 cells with EGF at 80 ng/mL significantly upregulated the NF-κB promoter activity whereas PDTC at 2.5 μM significantly reduced the NF-κB promoter activity induced by EGF and PDTC at 50 μM dramatically reduced the NF-κB promoter activity (A, due to cell apoptosis). EGF-induced NF-κB promoter activity was significantly enhanced by p65 at 1.4 μg/mL but abrogated by IκBαM at 1.4 μg/mL in OC1 cells (B). EGF and p65 additively regulated the NF-κB promoter activity in OC1 cells and p65 had a potent effect on the NF-κB promoter activity. Flow cytometry for Annexin-V and 7-AAD demonstrated that EGF had a significant effect on cell viability compared with control and the action was abrogated by PDTC (C). It is noted that PDTC at 50 μM was apoptotic to OC1 cells. *p<0.05. Med, MEM media without supplements; Ctrl, control. It is also noted that relative luciferase activity (RLA) is different between data sets A and B due to transfection efficiency between these two independent experiments: β-gal in data set A is less efficient than that in data set B. n=total samples from 3 separated experiments.