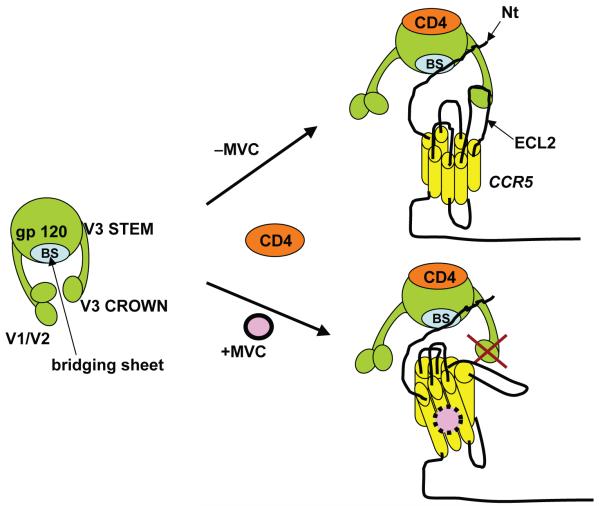
Figure 2. Model for maraviroc mechanism of action.
Binding of HIV-1 gp120 to CD4 exposes the bridging sheet and creates a coreceptor binding site. In the absence of maraviroc, the bridging sheet and the base of V3 interact with the N-terminus of CCR5, while more distal regions of V3 interact with extracellular loops (mainly ECL2). Binding of maraviroc to the transmembrane region of CCR5 locks CCR5 in a conformation that does not recognize the distal regions of V3.