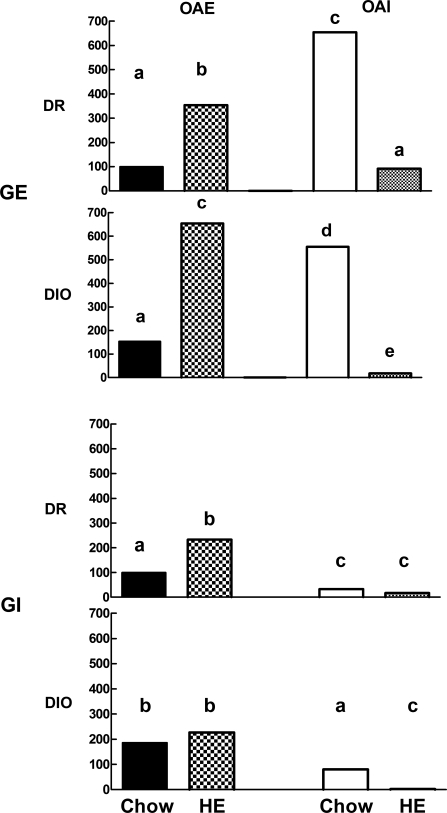
Fig. 3.
Dissociated VMN neurons from offspring of DIO and DR dams fed chow or HE diet through gestation and weaning (n = 5–7 rats/group) were categorized using calcium imaging as being GE or GI and then as being excited (OAE) or inhibited (OAI) by 15 mM oleic acid. This figure summarizes the data presented in Table 2, where each bar represents the mean percentage of GE or GI VMN neurons that were OAE or OAI in offspring of chow- and HE diet-fed DR vs. DIO dams. Bar heights are expressed as the mean percent of the DR chow-fed OAE neurons for all GE neurons (top two bar graphs) and all GI neurons (bottom two bar graphs). Bars for GE neurons from DIO and DR offspring with differing letters differ from each other by P = 0.05 or less. Similarly, bars for GI neurons from DIO and DR offspring with differing superscripts differ from each other by P = 0.05 or less.