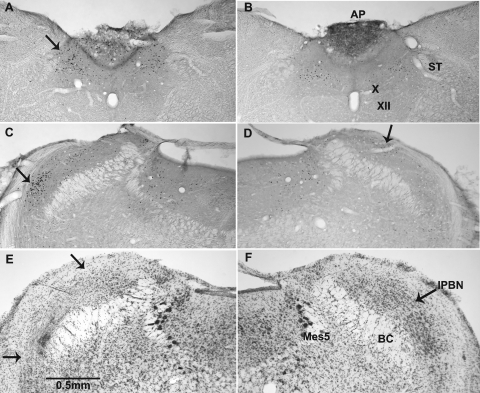
Fig. 1.
Digital photomicrographs of 50-μm coronal sections through the caudal medulla (A and B) and dorsal pons (C–F). A–D: photomicrographs from brains processed for immunohistochemical identification of c-Fos protein in experiment 1. E and F: photomicrographs from brains stained with cresyl violet in experiment 2. A and C: photomicrographs from rats treated with cisplatin. B and D: photomicrographs from those treated with saline. Arrows in A, C, and D indicate the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS), the ventrolateral, or external, lateral parabrachial nucleus (lPBNv), and the lateral, dorsal parabrachial nucleus (lPBNd), respectively. Panel E depicts the extent of the ibotenic acid lesion in the lPBN (between the arrows). F: section from a control rat at the same rostrocaudal level of the PBN. The value of the line in E is approximate because the immunohistochemical processing shrinks sections 15–20% more than cresyl violet. AP, area postrema; BC, brachium conjunctivum; Mes5, mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus; ST, solitary tract; X, dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus; XII, hypoglossal nucleus.