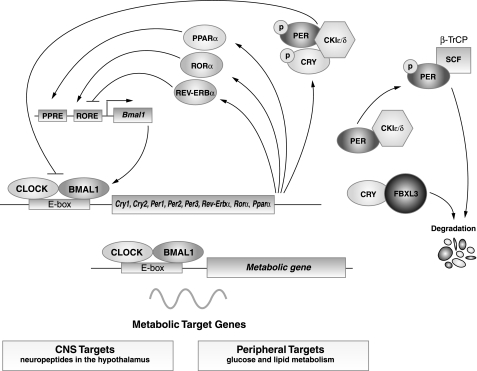
Fig. 1.
Core circadian clock network. The core molecular clock machinery is encoded by interlocking transcription-translation feedback loop that oscillates with a 24-h periodicity. The core mammalian clock comprises transcription factors CLOCK and BMAL1, which heterodimerize to drive the transcription of downstream target genes containing E-box enhancer elements. Among these, the period (PER) and cryptochrome (CRY) proteins then multimerize and inhibit the action of the CLOCK:BMAL1 complex, resulting in a rhythmic oscillation of the core clock genes and many of their downstream targets. In addition, the CLOCK:BMAL1 heterodimer also drives the transcription of metabolic target genes in the central nervous system (CNS) and in the peripheral tissues. CKIε/δ, casein kinase I-epsilon and -delta; ROR, retinoid-related orphan receptors; RORE, ROR-binding element; PPARα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α; SCF, Skp/Cullin/F-box.