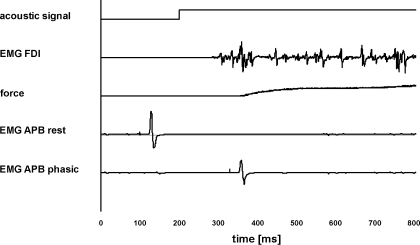
Fig. 1.
Motor task. The acoustic signal, EMG recording from first dorsal interosseus muscle, and the force produced by the index finger flexion are shown, as well as the 2 different conditions for abductor policis brevis muscle (APB) [transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) given at rest and during the phasic phase]. In one condition (EMG APB rest), TMS was given 100 ms after the beginning of the recording, which means it was given before the acoustic signal (at 200 ms after the beginning of the recording). In the other condition (EMG APB phasic), TMS was applied 20 ms before the first peak of EMG in first dorsal interosseus muscle (FDI) (phasic phase; in this subject, at 130 ms after the acoustic signal). Motor-evoked potential (MEP) size in APB decreased during the phasic phase compared with at rest.