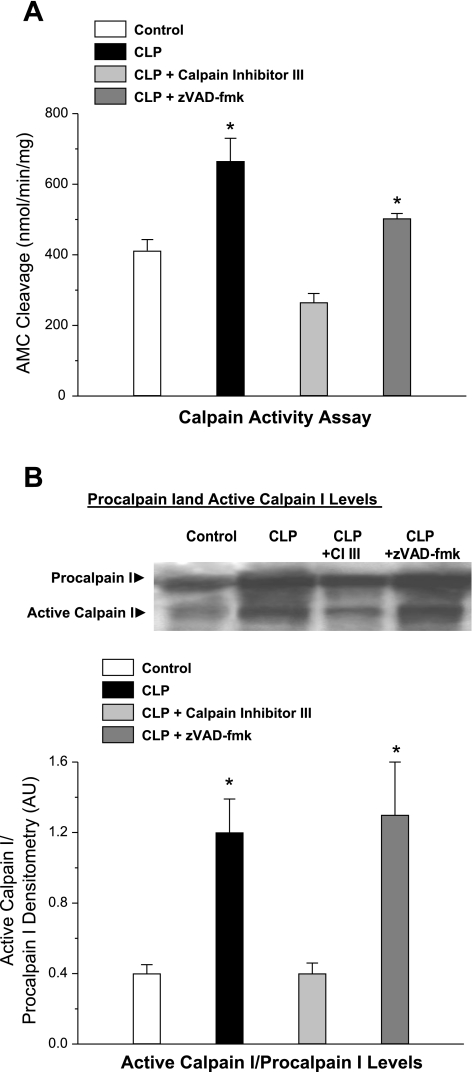
Fig. 2.
Diaphragm calpain activation. Calpain activity was assessed by determining the cleavage of a fluorogenic substrate by diaphragm homogenates (A) and by using Western blotting (B) to determine intact and cleaved calpain I protein levels for diaphragm homogenates from control, CLP, CLP plus CI III, and CLP plus zVAD-fmk groups. A: diaphragm samples from CLP animals (solid bar) had higher calpain activities than samples from control animals (open bar) (P < 0.02). Administration of CI III to CLP animals (light shaded bar) reduced calpain activation (P < 0.01), but administration of zVAD-fmk, a caspase inhibitor, had no effect on calpain activation in CLP animals (dark shaded bar). B: CLP also resulted in an increase in cleaved calpain I protein (P < 0.02 for comparison to control). Administration of CI III to CLP animals reduced cleaved calpain I protein levels (P < 0.02), whereas administration of zVAD-fmk did not. *Significant statistical difference compared with the control group, P < 0.05.