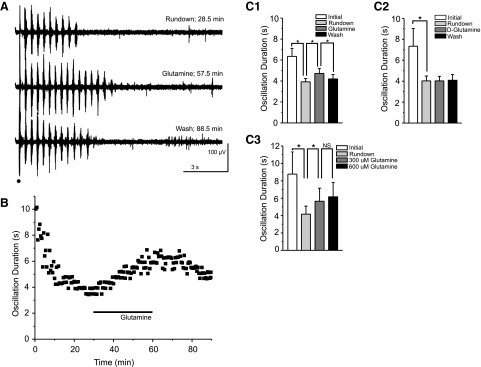
Fig. 4.
Exogenous glutamine (300 μM) partially and reversibly rescues evoked oscillations. A and B: sample traces (A) and time course of a typical experiment (B) show rundown of oscillation duration, the rescue effect of exogenous glutamine, and the secondary rundown that occurs after wash of glutamine. Stimulus is indicated by black dot and glutamine application by black bar. C: averaged durations at initial (00:00–02:30), rundown (27:30–30:00), glutamine (57:30–60:00), and wash (87:30–90:00) time bins show rundown and the reversible effect of glutamine (C1; 300 μM; *P < 0.0001, RM ANOVA; error bars indicate SE), but not d-glutamine (C2; 300 μM; *P > 0.05, RM ANOVA; error bars indicate SE) on oscillation duration. C3: averaged durations at initial (0–2.5 min), rundown (27.5–30 min), 300 μM glutamine (57.5–60 min), and 600 μM glutamine (87.5–90 min) time bins show no additional rescue of oscillation duration with an increased glutamine concentration (n = 5; P > 0.05, RM ANOVA).