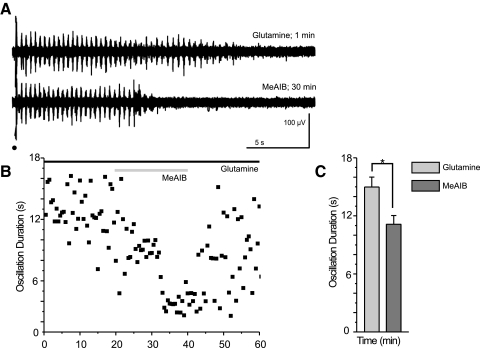
Fig. 5.
Blocking uptake of glutamine into neurons causes oscillation run down. A and B: sample traces (A) and the time course of a typical experiment (B) show a reduction in oscillation duration after application of the system-A transporter antagonist, α-(methylamino) isobutyric acid (MeAIB), in the presence of glutamine. Stimulation is indicated by a black dot, glutamine application by a black bar, and MeAIB application by a gray bar. C: averaged durations, at times of equilibrium glutamine (0–2.5 min) and MeAIB (17.5–20.83 min after MeAIB application) effect, show that MeAIB causes a reduction in oscillation duration even in the presence of exogenous glutamine (*P < 0.05, signed rank test, error bars indicate SE).