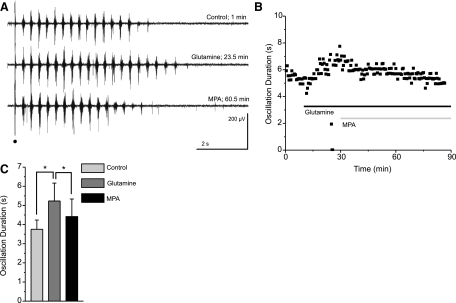
Fig. 6.
Blocking the conversion of glutamate into GABA reverses the glutamine-dependent rescue of evoked oscillations. A and B: representative traces (A) and the time course of a typical experiment (B) show glutamine-dependent rescue of rundown followed by a secondary run down in the presence of 3-mercaptoproprionic acid (MPA), a glutamate decarboxylase inhibitor. Stimulation is indicated by a black dot, glutamine application by a black bar, and MPA application by a gray bar. C: averaged durations at times of equilibrium control (0–2.5 min), glutamine (22.5–25 min), and MPA (60–62.5 min) effect show the rescue effect of glutamine and the reversal of that effect by application of MPA (*P < 0.01, RM ANOVA, error bars indicate SE).