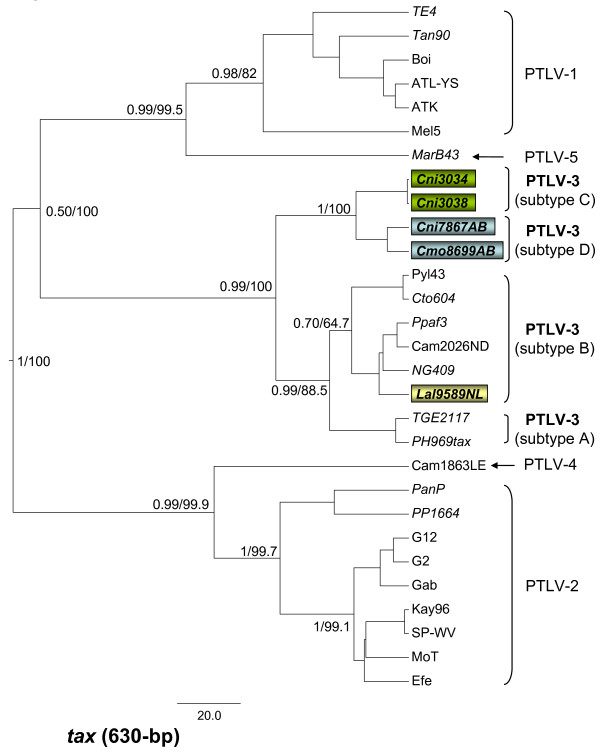
Figure 4.
Identification of a highly divergent STLV-3 subtype inferred by phylogenetic analyses of partial PTLV tax sequences (630-bp). First and second codon positions were used to generate PTLV phylogenies by sampling 10,000 trees with a Markov Chain Monte Carlo method under a relaxed clock model, and the maximum clade credibility tree, i.e. the tree with the maximum product of the posterior clade probabilities, is shown. Maximum likelihood trees were also inferred using the program PhyML and identical tree topologies were obtained with both methods. Posterior probabilities of inferred Bayesian topologies (numerator) and bootstrap support (1,000 replicates) for PhyML topologies (denominator) are provided at major nodes. STLV-3d and other new sequences generated in the current study from STLV-3c and STLV-3b-infected animals are boxed. Branch lengths are proportional to median divergence times in years estimated from the post-burn in trees with the scale at the bottom indicating 20,000 years.