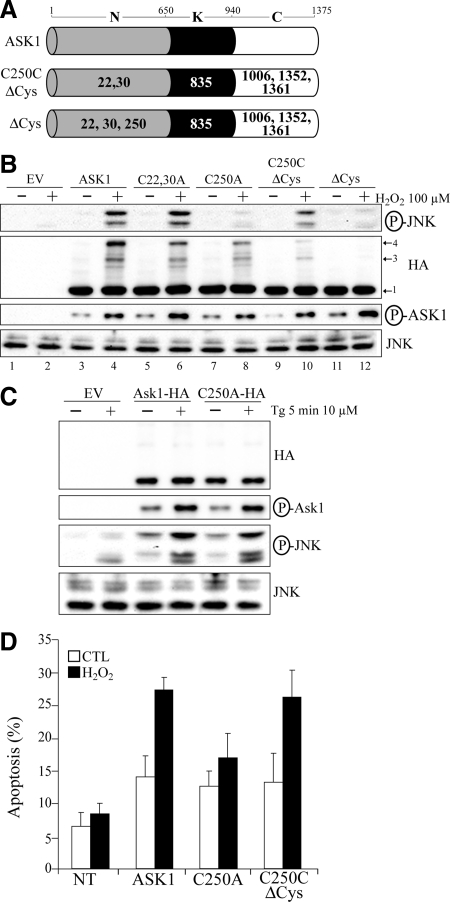
Figure 4.
ASK1 Cys250 is essential for ASK1-dependent activation of JNK and induction of apoptosis by H2O2 in vivo. (A) Schematic representation of the different cysteine substitution mutants used. Represented are the N-terminal (N), kinase (K), and C-terminal (C) domain of ASK1. Residue numbers at domain boundaries are indicated. Numbers in bold or in white within each domain indicate which cysteine residue(s) have been replaced by alanine residue(s). (B through D) 293T (B and C) or HeLa (D) were transfected with the empty vector pcDNA3 (EV in C), various ASK1 constructs defined in A or with other ASK1 mutants labeled “Cx,yA” where the x and y indicates the positions of cysteines residues replaced by alanine residues. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were left untreated ([−] in B and C or CTL in D) or exposed ([+] in B and C) to 100 μM H2O2 for 3 min in (B), 500 μM H2O2 for 3 h in (D), or 10 μM thapsigargin (Tg) for 5 min in (C). In B and C, total cell extracts were migrated on nonreducing gels and immnunoblotted with anti-HA or migrated on reducing gel and probed with anti-JNK or either anti-phospho specific ASK1 (P-ASK1) or JNK (P-JNK). Band 1 indicates the expected positions of monomeric ASK1 (150 kDa) and bands 3 and 4 point the position of ASK1 DBM. In D, the percentage of HA-positive cells showing condensed or fragmented nuclei was determined by immunofluorescent microscopy. The nontransfected condition (NT) consist of cells showing no signal for anti-HA by immunofluorescent microscopy in conditions where ASK1-HA was transfected. The data are means±SEM from three distinct experiments. P values of <0.05 were obtained (two-tailed paired t test) when percentages of apoptosis from cells transfected with C250A were compared with those of cells transfected with ASK1 or C250CΔCys after H2O2 treatment.