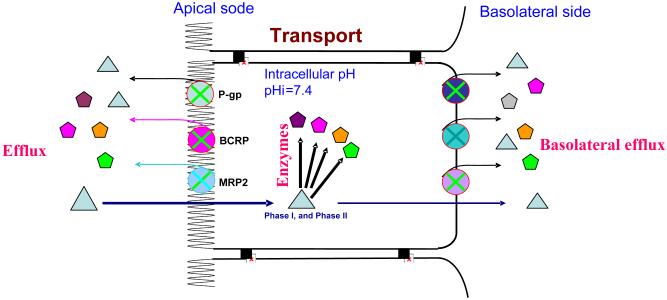
Fig. 7.
Schematic representation of the more complex coupling theories. Substrates are represented by triangles whereas products of enzymes or metabolites are represented by other shapes. In this scheme, substances such drugs and nutrients will get in by passive diffusion or carried by transporter. The intake process at the apical side is often called uptake, whereas intake at the basolateral side is often a part of secretion. In contrast to intake, substances excreted by transporters out of the cells is called efflux. These efflux transporters can locate at either sides (apical or basolateral side). Some efflux transporters such as p-gp, MRP2, MRP4, and BCRP are generally present on the apical surface of the cells, whereas others such as MRP3, MRP5, MRP6 are localized on the basolateral of the cell. Some efflux transporters such as MRP1 and OATs are present on both apical and basolateral surfaces. Efflux transporters located at the apical side diminish absorption into the blood and facilitate excretion, whereas efflux transporters at the basolateral sides have the opposite functions.