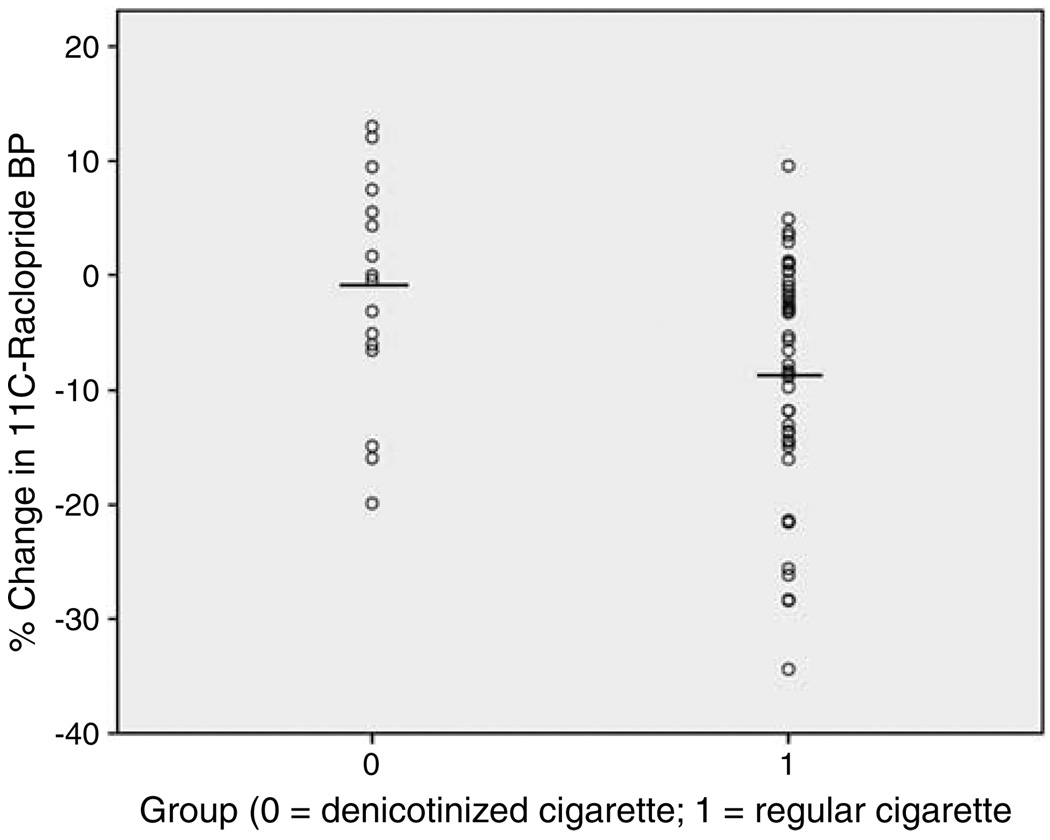
Figure 1.
Scatterplot showing percent change in 11C-raclopride binding potential (BP) for the group that smoked a denicotinized cigarette (−1.2 ( ± 2.5)%; n = 16) and the group that smoked a regular cigarette (−8.4 ( ± 1.5)%; n = 46). The group that smoked a denicotinized cigarette had less of a decrease in 11C-raclopride BP than the group that smoked a regular cigarette, indicating that nicotine inhalation is important for dopamine release.