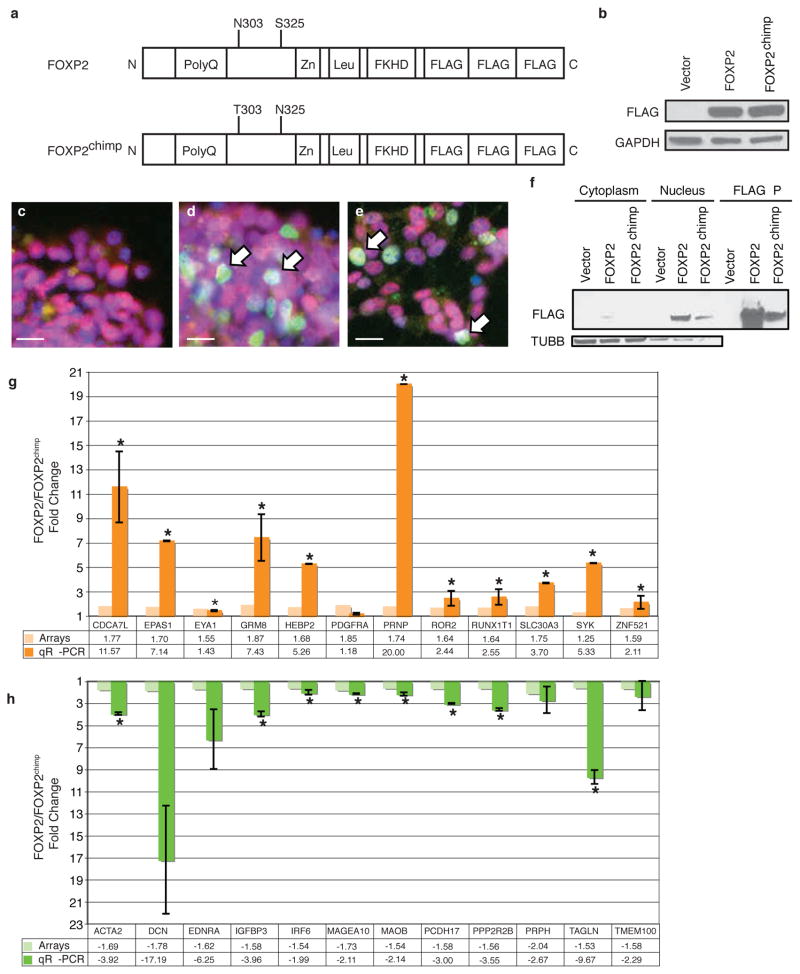
Figure 1.
FOXP2 and FOXP2chimp differentially regulate genes in SH-SY5Y cells. a) Schematic of human FOXP2 showing its major functional protein domains and the two amino acid changes in the mutant FOXP2chimp. b) Representative immunoblot for FLAG-tagged FOXP2 and FOXP2chimp stable overexpression in SH-SY5Y cells. c–e) Immunofluorescent staining of antibodies against FLAG epitope (green) and FOXP1 (red), and DAPI (blue) for nuclei. c) Vector cells demonstrate no FLAG expression, while both FOXP2 (d) and FOXP2chimp (e) expressing cells have FLAG-tagged FOXP2 in the cell nucleus. Scale bars are 5 microns. f) Subcellular fractionation followed by immunoblotting. g–h) Quantitative RT-PCR of genes that were differentially expressed in cells expressing FOXP2 compared to FOXP2chimp. Asterisks indicate P≤0.05 and error bars are ± s.e.m. (two-tailed Student’s t-test, n=3 or 4).