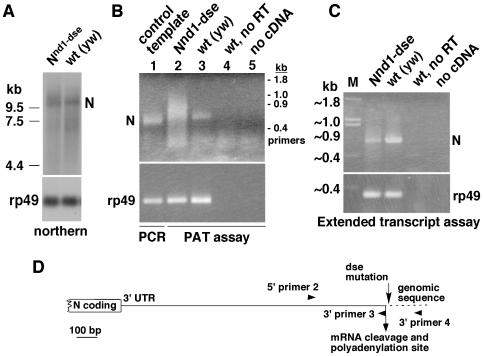
Figure 4. Nnd1-dse embryos produce higher levels of poly(A)-tailed N mRNA and Nintra.
(A) Northern blots showing comparable levels of N mRNA in Nnd1-dse and wild type embryos after 60 minutes at the restrictive temperature of 30°C. (B) PAT assay using N specific (5′ primer 2) or rp49 specific primer and an oligo d(T) primer that reveals the level of polyadenylation of N mRNA (top panel) and the control rp49 mRNA (bottom panel). The smear of fragments of heterogeneous lengths that is present only in the Nnd1-dse lane indicates that N mRNA is poly(A)-tailed to a higher level in Nnd1-dse embryos than in wild type embryos. Lane 1 is the product of PCR using N cDNA template (control template) and an N primer (3′ primer 3) ending at the N mRNA cleavage site. Ethidium bromide gel images are shown. no RT = reverse transcriptase omitted in the cDNA synthesis reaction. rp49 = rp49 PAT fragments amplified from the same samples that served as controls. (C) Unprocessed (extended) transcript assay using one primer upstream of the mRNA cleavage site (5′ primer 2) and one primer downstream of the cleavage site (3′ primer 4). Only N transcripts that bypass the consensus poly(A) site are expected to be amplified. To assess the level of total RNA in the reactions, primers located within the rp49 cDNA were used. Ethidium bromide gel images are shown. D. Schematic representation of the primers used for results presented in B and C.