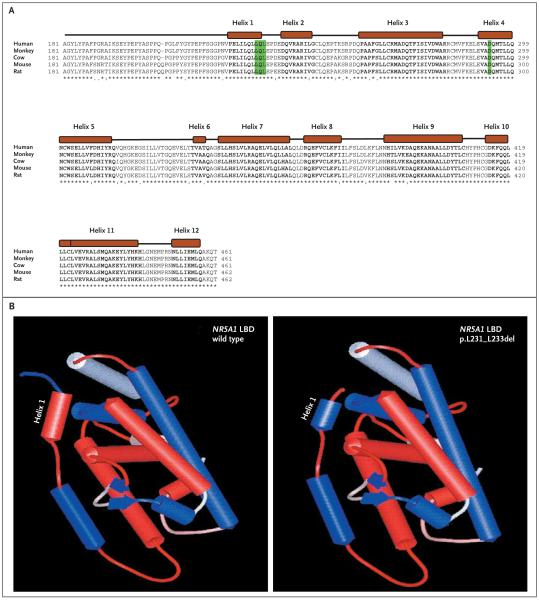
Figure 3. Comparison of Sequence Alignment of Portions of the Human NR5A1 Protein with Those of Other Mammals and 3-D Models of Wild-Type and Mutated NR5A1 Proteins.
In Panel A, sequence alignment of the distal portion of the hinge and the ligand-binding domain (LBD) of human NR5A1 protein is compared with those of other mammals. The 12 predicted alpha helixes in the ligand-binding domain of NR5A1 are indicated as solid boxes, and amino acids in bold text. The position of the p.Asp293Asn missense mutations and the deletions of three amino acids (p.Leu231_Leu233) are highlighted. Both mutations fall either in the highly conserved Helix 1 (p.Leu231_Leu233) or in Helix 4 (p.Asp293Asn) of the ligand-binding domain. In Panel B, three-dimensional models of the ligand-binding domain of both the wild-type and p.Leu231_Leu233del mutated NR5A1 proteins were obtained with the use of the Web-based interface 3D-JIGSAW (for details, see the Supplementary Appendix). The hydrophobic helixes are shown in red, and the hydrophilic helixes in blue. Note the change of Helix 1 from hydrophobic to hydrophilic in the p.Leu231_Leu233 deletion mutant.