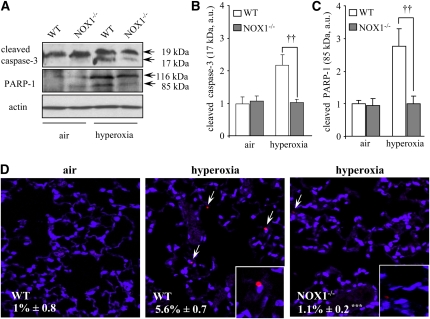
Figure 6.
Active caspase-3 and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP)-1 cleavage are reduced in the lungs of hyperoxia-exposed NADPH oxidase-1 (NOX1)-deficient mice. (A) Cleaved caspase-3 (17 kD) and cleaved PARP-1 (85 kD) proteins were detected in lung homogenates of NOX1−/− and wild-type (WT) mice exposed to air or hyperoxia for 72 hours. β-Actin–immunoreactive bands were used to demonstrate equal loading. These gels were representative of all samples analyzed (n = 5 per group). (B and C) Densitometric quantification of cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved PARP-1 protein levels was expressed as fold increase compared with WT air sample (set as 1). Each sample was normalized with β-actin loading. Columns and error bars represent means and SEM (n = 5; ††P < 0.01, NOX1−/− vs. WT mice in hyperoxia). (D) Representative merged images of lung sections stained with anti–cleaved caspase-3 (red) and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (blue) from WT and NOX1−/− mice (n = 3). Original magnification, ×40. ***P < 0.001, NOX1−/− vs. WT mice in hyperoxia.