Fig. 1.
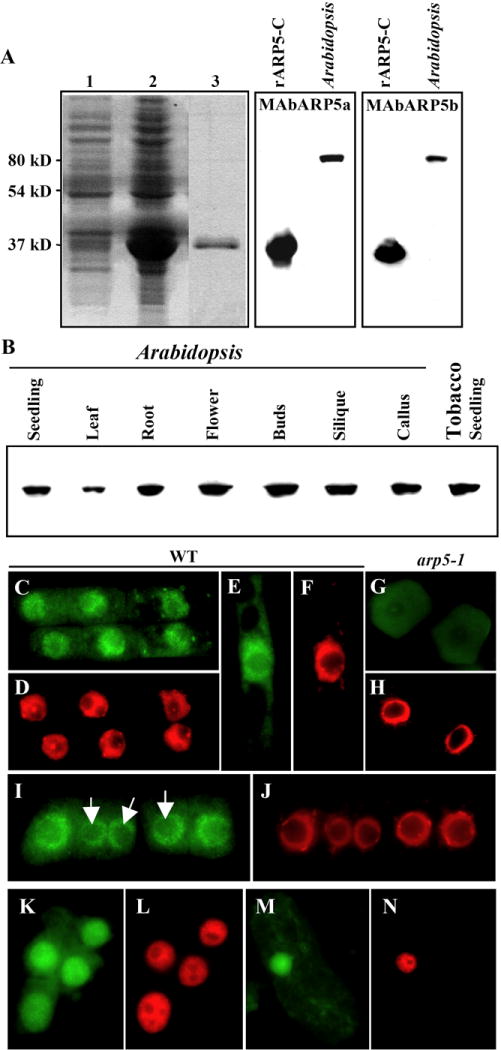
Expression and nuclear localization of ARP5 protein. (A) Reactivity of ARP5 antibodies MAbARP5a (middle panel) and MAbARP5b (right panel) with the truncated 32 KDa recombinant ARP5 (rARP5-C) and the native full length (80 KDa) ARP5 in the Arabidopsis seedling extract. An image of a coomassie brilliant blue stained gel showing the expression of the truncated ARP5 is depicted in the left panel. Lane 1, Control BL21 cells containing empty pET15b vector; lane 2, BL21 cells expressing ARP5 containing pET15b vector; Lane 3, Purified recombinant rARP5-C protein. (B) Western blot analysis of ARP5 in different organs and callus tissue of Arabidopsis with MAbARP5a. ARP5 homolog in tobacco seedling extract is shown in the last lane. (C-N) Immunocytochemical localization of ARP5 with MAbARP5a (C, G, I, K, M) and MAbARP5b (E) in root (C-L) and leaf cells (M, N). (C-J) Arabidopsis, (K-N) tobacco. (G, H) represent arp5-1 mutant cells and the rest are wild type (WT) cells. ARP5 staining with FITC-conjugated anti-mouse secondary antibody is shown in green and DNA staining with DAPI is shown in red. Arrows in I point to the nucleoli.
