Figure 6.
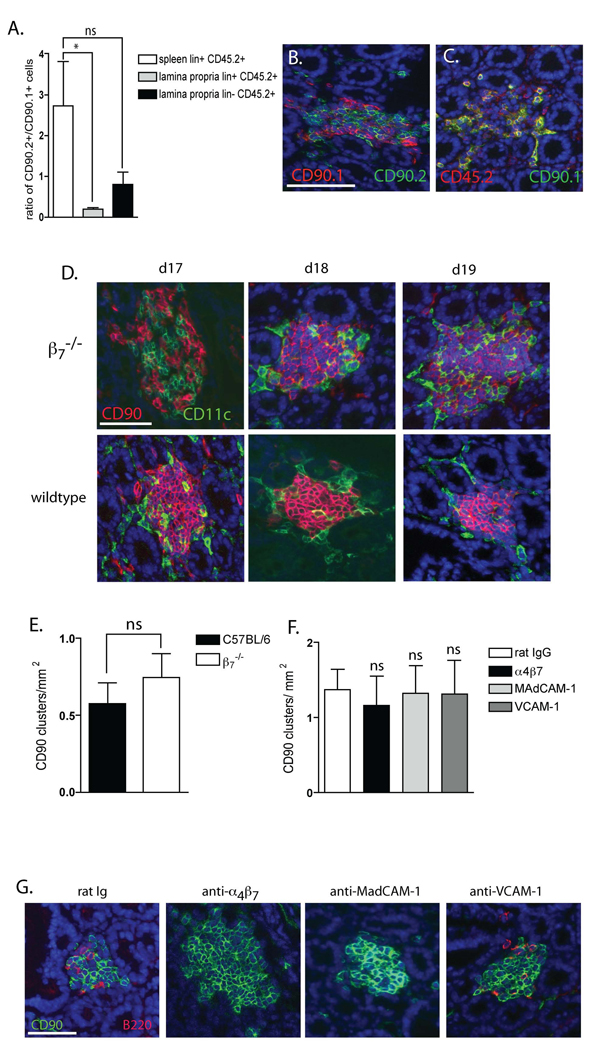
β7 plays a redundant role in localizing LTi-like cells to the small intestine and a non-essential role in CP development in neonatal mice. To more definitively address the role for β7 in localizing the CD90+ cells to the small intestine and CP we performed competitive transfers of wildtype (CD90.1, CD45.2) and β7−/− (CD90.2, CD45.2) bone marrow into wildtype (CD90.2, CD45.1) recipients. Recipients were analyzed to identify the origin of CD45.2 (donor) lin+ CD90+ and lin− CD90+ cells with flow cytometry and with immunohistochemistry to evaluate the localization of wildtype and β7−/− CD90+ cells to the CP. Flow cytometric analysis of gated on the CD45.2+ (donor) population revealed an enrichment of lin+ CD90+ cells of β7−/− origin (CD90.2) in the spleen while conversely the lamina propria contained significantly fewer CD45.2+ (donor) lin+ CD90+ cells of β7−/− origin (panel A). There were too few lin− CD90+ splenocytes for analysis, however the donor (CD45.2+) lin− CD90+ cells in the lamina propria were relatively lacking in cells from β7−/− donors (CD90.2) in comparison to cells from wildtype donors (CD90.1) (panel A). This did not reach statistical significance when compared with the origins of lin+ donor splenocytes. Immunohistochemistry revealed equal populations of CD90.1+ (wildtype donor origin) and CD90.2+ (β7−/− donor origin or recipient origin) cells in the CP (panel B). The donor (CD45.2+) CP cells were largely from wildtype donors (CD90.1+) (yellow co-staining panel C), thus demonstrating a relative deficiency of β7−/− cells to compete for this niche. To evaluate a role for β7 in the development of CP in the neonatal period, we examined small intestines from neonatal wildtype and β7−/− mice and wildtype mice given blocking antibodies to α4β7, MAdCAM-1, VCAM-1 or control IgG from day 17 of gestation until analysis at day 19 of neonatal life. CP are detectable in both wildtype and β7−/− mice on day 17 of neonatal life (panel D), and there was no difference in the density of CP on day 19 of neonatal life when CP formation is rapidly increasing in β7−/− mice (panel E) or mice given blocking antibodies to α4β7, MAdCAM-1, or VCAM-1 (panel F). Consistent with the observation of antibody blockade in adult mice, we observed that anti-α4β7 and anti-MadCAM-1 inhibited the influx of B-lymphocytes into the cellular clusters and anti-VCAM-1 had no effect on B-lymphocyte influx into the cellular clusters at day 19 of neonatal life (panel G). Data in panels A and E is generated from 4 mice in each group. Data in panel F is generated from 3 mice in each group. * = p<0.05, ns= not significant. The scale bar panel B = 100µm, panel D = 50µm, and panel G = 50µm.