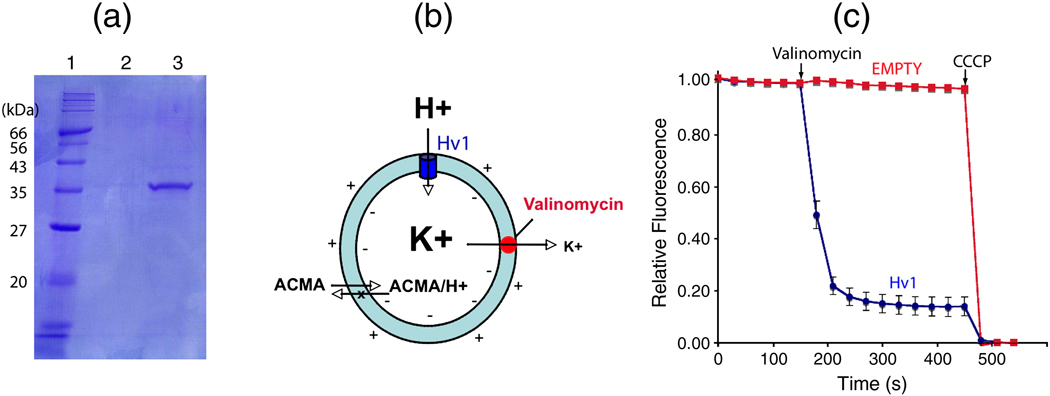
Fig. 1.
Proton flux by vesicles containing recombinant Hv channels. (A) SDS-PAGE gel showing purified Hv channels. Lane 1: molecular weight marker, 2: final wash, and 3: Human Hv-1D4 eluted with 0.4 mg/ml 1D4 peptide. The gene for the full length human Hv channels (GenBank accession no: 91992153) with a C-terminal 1D4 tag (ARAAGGTETSQVAPA) was ligated into the PICZ-c vector (Invitrogen Life Technologies). This vector was transformed into a His+ strain of SMD1163 Pichia pastoris and selected as described 6. Transformed cells were grown in 1 L cultures of BMG media (Yeast Nirtogen Base, 100 mM sodium phosphate pH 6.3 and 1 % glycerol) at 30 ° C until an optical density of ~20 was reached. BMG media was exchanged for BMM media (BMG with 1 % MeOH instead of glycerol) and grown at 24° C for 24 hours. Frozen pellets were lysed with a mixer mill (Retsch, Inc. Model MM301) and resuspended in buffer (500 mM NaCl, 50 mM TRIS-HCl, pH 8.5, 2 mM β-mercaptoethanol, 0.1 µg/ml deoxyribonuclease I, 0.1 µg/ml pepstatin, 1 µg/ml leupeptin, 1 µg/ml aprotinin, 1.0 mM phenylmethysulfonyl fluoride and 2.0 mM Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). The pH was adjusted to 8.5 with NaOH, and 0.15 g DDM (n-dodecyl-β-D-maltopyranoside, Anatrace) per g of cells was added prior to a 2–3 hour extraction at room temperature followed by centrifugation at 31000 × g for 25 min. Supernatant was added to 1D4 antibody-linked sepharose affinity resin previously equilibrated with buffer A (500 mM NaCl, 50 mM TRIS-HCl, pH 7.5, 1 mM EDTA and 1 mM DDM) and rotated at room temperature for 2 hours. The resin was collected on a column, washed with buffer A (4 × 5 column volumes) and eluted with buffer A containing 0.4 mg/ml 1D4 peptide. Protein was loaded on a Superdex-200 gel filtration column in 20 mM TRIS-HCl, pH 7.5, 150 mM KCl, 50 mM NaCl and 4 mM DM (n-decyl-β-D-maltopyranoside, Anatrace, anagrade) (Buffer B). The fractions corresponding to Hv channels were pooled and concentrated to 1.0 mg/ml for reconstitution into lipid vesicles. (B) Fluorescence-based H+ flux assay. Vesicles (cyan) loaded with high concentration of K+ are diluted into low concentration K+ buffer containing the fluorescence dye ACMA (9-amino-6-chloro-methoxyacridine). Addition of valinomycin (red), a K+ selective ionophore, results in K+ efflux, which generates a driving force for H+ influx. If there is a H+ channel (blue) in the vesicle membrane, pH inside the vesicle will decrease. This pH decrease is monitored by ACMA because the protonated form, which becomes trapped inside vesicles, loses fluorescence whereas unprotonated ACMA diffuses freely across the membrane 9. (C) Fluorescence-based H+ flux assay for vesicles with and without Hv1 colored blue and red, respectively (n = 5). Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. Valinomycin and CCCP are added at the indicated time points. The fluorescence data for vesicles containing Hv channels was obtained using a published procedure with the following modification 16. A mixture of 6:6:3:3:1 of POPC:POPE:POPS:SM:PI (1-Palmitoyl-2-Oleoyl-sn-Glycero-3-Phosphocholine, 1-Palmitoyl-2-Oleoyl-sn-Glycero-3-Phosphoethanolamine, 1-Palmitoyl-2-Oleoyl-sn-Glycero-3-Phospho-L-Serine, Sphingomyelin, and L-α-Phosphatidylinositol, obtained from Avanti) was prepared based on the composition of human neutrophil plasma membrane 17. The lipid mixture was dried under an Argon stream and then resuspended to 10 mg/ml in dialysis buffer (20 mM HEPES, pH 7.0, 150 mM KCl, 10% glycerol, 0.2 mM EGTA and 2 mM 2-mercaptoethanol). The lipid mixture was then sonicated in a bath sonicator three times for 2 minutes. Decylmaltoside (DM) was added to the lipid mixture to 10 mM and rotated at room temperature for 1hr. Protein was added to the lipid mixture in a 1:100 (wt:wt) protein to lipid ratio and an additional 10 mM DM was added. As a control empty vesicles were made in which only buffer B was added to the lipids. The protein-lipid mixture was rotated at room temperature for ~3 hours then placed into dialysis membrane (molecular weight cut off of 50 KDa) and dialyzed in 4 L of dialysis buffer for 5 days at RT exchanging buffer daily. Vesicles were then harvested and flash frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80° C. Vesicles were thawed in room temperature water and then sonicated once in a bath sonicator for 5 seconds and then diluted 20 fold into flux buffer (20 mM HEPES, pH 7.0, 150 mM NaCl, 7.5 mM KCl, 10% glycerol, 0.2 mM EGTA, 0.5 mg/ml BSA, 2 mM 2-mercaptoethanol and 2 µM ACMA) in a quartz cuvette. Data were collected on a Spex Fluorolog 3–11 spectrofluorometer in time acquisition mode at 30-second intervals with excitation at 410 nm, emission 490 nm, with bandwidth 5 nm and an integration time 2 s. A baseline was collected for 150 s before the addition of 20 nM valinomycin. After the fluorescence stabilized carbonyl cyanide m-chloro phenyl hydrazone (CCCP) was added to 2 µM rendering all vesicles H+ permeable and a minimum baseline was collected for 150 seconds. Data are scaled by (Fi − Fmin)/(Fmax−Fmin), where Fmax is the average value of the starting baseline and Fmin is the average value of the minimum baseline. Fmax−Fmin (the total reduction in fluorescence after CCCP addition) was ~ 25 % for all vesicles.