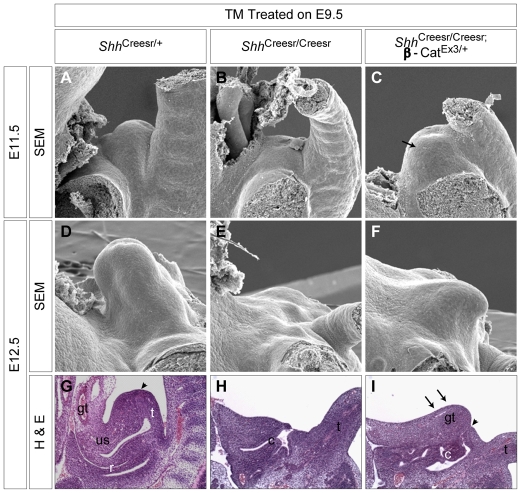
Fig. 5.
Phenotypic analysis of dUE-rescued Shh-/- GTs. (A-C) SEM analysis of E11.5 control (A), Shh-/- (B) and dUE-rescued Shh-/- (C) mouse embryos showing agenesis of the GT in Shh-/- (B) and prominent GT growth in the rescued Shh-/- (arrow in C). (D-F) SEM analysis of E12.5 embryos of the genotypes indicated showing that the rescued GT (F) was much smaller than in the wild type (D). (G-I) H&E staining on mid-sagittal sections of E12.5 embryos showing a considerable dorsal growth (arrows in I) and a persistent cloaca in the dUE-rescued Shh-/-. The distal end of the UE is indicated by arrowheads in G,I. gt, genital tubercle; us, urogenital sinus; r, rectum; c, cloaca; t, tail.