Figure 2.
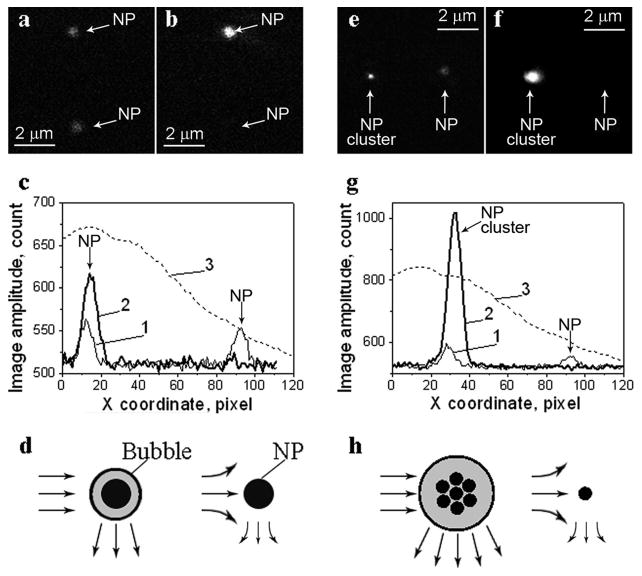
Optical scattering time-resolved images of gold spheres; left panel (a,b)—a pair of identical 250 nm gold NPs, right panel (e,f)—a pair of a single 90 nm NPs and a cluster of 90 nm NPs; (a) and (e)—pulsed scattering images obtained without a pump pulse; (b) and (f)—pulsed scattering images obtained at a delay of 9 ns after the pump pulse (532 nm, 0.5 ns); (c) and (g)—the spatial profiles of the pump beam fluence show the difference in the irradiation of two NPs (3) and of the image pixel amplitudes for the images shown in (a), (b), (e), and (f), respectively: 1—scattering signal amplitude obtained without a pump pulse corresponds to (a) and (e), 2—scattering signal amplitude obtained with a pump pulse corresponds to (b) and (f); (d) and (h)—the schemes illustrating the possible mechanisms of thermal influence on scattering during evaporation (the bubble amplifies the scattering) and heating (the scattering of the probe beam by the thermal gradients of the refractive index of the NP environment) of the NP environment.
