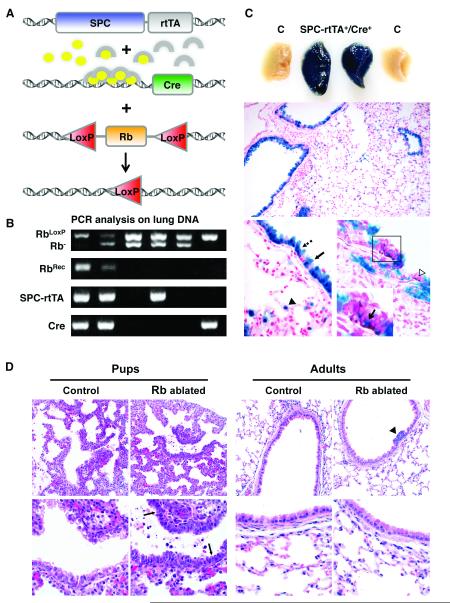
Figure 1. Epithelial hyperplasia and cell death seen in Rb ablated lungs at birth is not present in adult lungs.
A, SPC-rtTA+/−/tetCre+/− double transgenic mice were bred to RbLoxP/LoxP or RbLoxP/− mice. Doxycycline (ovals) activates the rtTA (arches) expressed specifically in lung epithelium leading to Cre expression and subsequent recombination at floxed Rb alleles. B, PCR analysis on lung DNA from day 1 pups. Rb recombination (RbRec) of floxed Rb alleles (RbLoxP) is only detected in lungs from mice containing both transgenes (SPC-rtTA, Cre). Mice were homozygous for the floxed Rb allele or heterozygous for the floxed and germline knockout (Rb−) alleles. C, Whole mount ß-galactosidase staining on lungs from day 1 mice pups containing the ROSA26 reporter locus demonstrates uniform staining in double transgenic lungs (SPC-rtTA+/Cre+) but not in controls lacking one or both transgenes (C). ß-galactosidase staining is restricted to the epithelium and present in Clara (arrow), ciliated (dashed arrow) and type II cells (arrowhead) in adult lungs. A subset of CGRP positive epithelial cells (brown, boxed area and open arrowhead) stain for ß-galactosidase (arrow in inset designates double positive cell). n ≥ 3 mice for each group. Original magnification: 200x (middle), 1000x (bottom). D, Hematoxylin and eosin stained lung sections show epithelial hypercellularity and apoptotic bodies (arrows) in Rb ablated E18.5 lungs (Pups) but not in Rb proficient lungs (Control) or Rb ablated lungs from 8 month old mice (Adults). Hypercellular neuroendocrine lesions are present in adult Rb ablated lungs (arrowhead). Original magnification: 400x (top row), 1000x (bottom row).