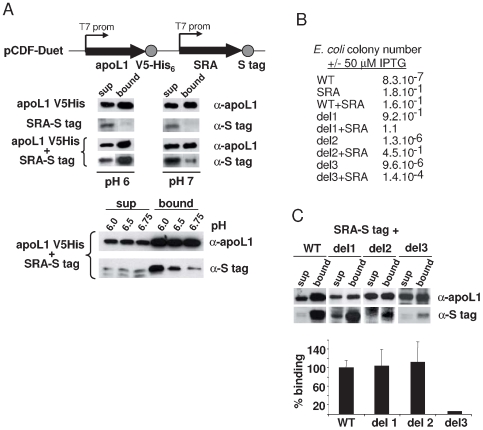
Figure 2. SRA interaction with apoL1.
A. Double expression of apoL1 and SRA in E. coli. The scheme of the plasmid construct is shown above Western blot data illustrating the detection of the two tagged proteins from the lysis supernatant (sup = supernatant) and their recovery in the fractions bound to nickel beads. ApoL1 and SRA were revealed by anti-apoL1 and anti-S tag antibodies, respectively. The pH of the extraction buffer was between 6 and 7, as indicated. B. Influence of apoL1 and/or SRA expression on bacterial plating efficiency determined by the ratio of colonies counted following induction versus non-induced controls, as illustrated in Fig. 1B. C. Evaluation of the level of protein association with the nickel beads. SRA binding to apoL1 was expressed as SRA binding percentage divided by the percentage of apoL1 binding to the nickel beads, which varied depending on the type of mutation/deletion performed on the protein. This ratio was considered as 100% for SRA binding to WT apoL1. In E. coli co-expressing WT apoL1 and SRA, the typical yield of each protein was respectively 3 µg and 100 ng/1010 cells. In this and the following figures, the values resulted from three independent experiments each performed in triplicate.