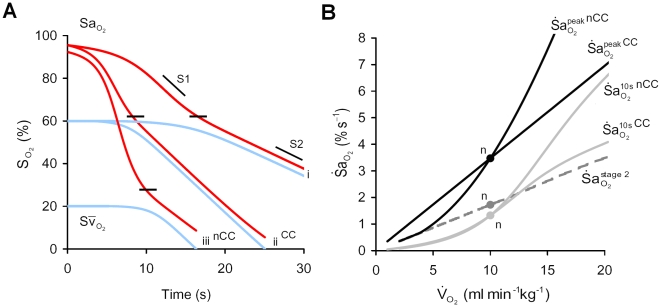
Figure 6. Impact of metabolic O2 consumption (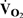 ) on
) on 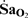 .
.
Panel (A) shows the effect of doubling 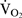 on arterial (
on arterial (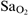 ) and mixed venous (
) and mixed venous (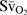 ) O2 during apnea; (i) 10 ml min−1kg−1, (ii) 20 ml min−1kg−1 with cardiac compensation (CC), and (iii) 20 ml min−1kg−1 with no CC (nCC). Note that with CC, increased
) O2 during apnea; (i) 10 ml min−1kg−1, (ii) 20 ml min−1kg−1 with cardiac compensation (CC), and (iii) 20 ml min−1kg−1 with no CC (nCC). Note that with CC, increased 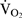 , from (i) to (ii), elevated
, from (i) to (ii), elevated 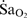 uniformly at all levels of
uniformly at all levels of 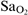 during both stages 1 and 2; note that the level of
during both stages 1 and 2; note that the level of 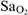 at the inflection point (shown by short black lines) is unchanged. With nCC (iii), increased
at the inflection point (shown by short black lines) is unchanged. With nCC (iii), increased 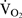 caused a reduced resting
caused a reduced resting 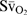 and lower
and lower 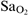 inflection, and greater
inflection, and greater 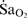 during stage 1, compared to (ii). (B) Sensitivity of
during stage 1, compared to (ii). (B) Sensitivity of 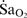 to changes in
to changes in 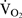 . Note that with increased
. Note that with increased 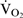 : a uniform increase in
: a uniform increase in 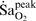 occurred with CC, and a more-than-proportional increase was seen with nCC;
occurred with CC, and a more-than-proportional increase was seen with nCC; 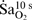 is elevated in both cases, but more so with nCC; a uniform increase in
is elevated in both cases, but more so with nCC; a uniform increase in 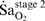 is shown regardless of CC. n = ‘normal’ values; S1, stage 1 slope; S2, stage 2 slope.
is shown regardless of CC. n = ‘normal’ values; S1, stage 1 slope; S2, stage 2 slope.