Figure 8. Impact of cardiac output (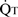 ) on
) on 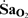 .
.
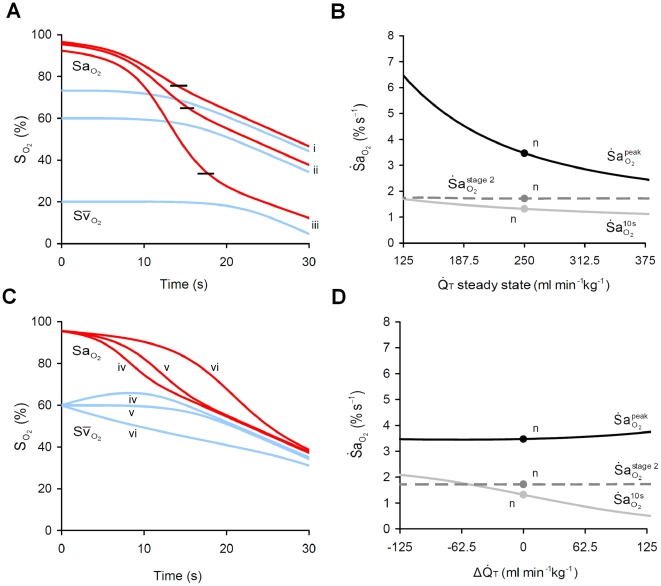
(A) Effect of three levels of resting 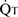 , (i) 375 ml min−1kg−1, (ii) 250 ml min−1kg−1, and (iii) 125 ml min−1kg−1, on arterial (
, (i) 375 ml min−1kg−1, (ii) 250 ml min−1kg−1, and (iii) 125 ml min−1kg−1, on arterial (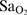 ) and mixed venous (
) and mixed venous (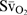 ) O2 during apnea. Note that reduced
) O2 during apnea. Note that reduced 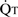 elevates
elevates 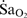 , associated with a reduction in resting
, associated with a reduction in resting 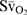 and reduction in
and reduction in 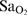 at the stage 1–2 transition or inflection point (shown by short black lines). (B) Sensitivity of
at the stage 1–2 transition or inflection point (shown by short black lines). (B) Sensitivity of 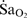 to changes in
to changes in 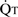 . Note the strong influence of
. Note the strong influence of 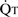 on
on 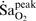 , but negligible effect on
, but negligible effect on 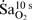 and
and 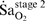 . (C) Simulations in (A) repeated for a step change in
. (C) Simulations in (A) repeated for a step change in 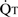 at apnea onset by (iv) +125 ml min−1kg−1 (e.g. tachycardia), (v) 0 ml min−1kg−1, and (vi) −125 ml min−1kg−1 (e.g. bradycardia), following resting
at apnea onset by (iv) +125 ml min−1kg−1 (e.g. tachycardia), (v) 0 ml min−1kg−1, and (vi) −125 ml min−1kg−1 (e.g. bradycardia), following resting 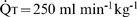 . Note that the transient effect of
. Note that the transient effect of 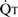 is opposite to the resting effect of
is opposite to the resting effect of 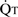 on arterial desaturation during apnea. (D) Sensitivity of
on arterial desaturation during apnea. (D) Sensitivity of 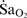 to acute changes in
to acute changes in 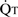 during apnea. Note the strong influence of a step-change in
during apnea. Note the strong influence of a step-change in 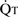 on
on 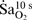 , but negligible effect on
, but negligible effect on 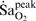 and
and 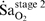 . n = ‘normal’ values.
. n = ‘normal’ values.