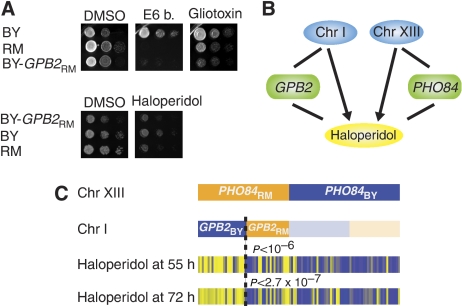
Figure 5.
Causal role of GPB2 in response to drugs. (A) Strains were grown overnight in YPD medium, diluted to OD600∼0.2 and plated with 10-fold dilution on YPD+drug media (see section Materials and methods). The top three panels are photos of YPD plates containing DMSO (control), E6 berbamine or gliotoxin. The bottom panels are photos of YPD plates containing DMSO or haloperidol. The results show a large difference in drug sensitivity between BY and RM. The AS strain (BY GPB2-RM) grows at a rate similar to the RM strain. (B) Camelot identifies two loci (Chromosome I: 1–55 329 and Chromosome XIII: 27 644–33 681) and causal genes encoded within these loci, GPB2 and PHO84, that are responsible for the response to haloperidol. (C) Analysis shows that GPB2 and PHO84 interact with each other to influence growth in the presence of haloperidol. Shown are the genotypes for PHO84 and GPB2, and growth in the presence of haloperidol. Segregants with both the PHO84-RM and GPB2-BY alleles have significantly better resistance (P-value from Wilcoxon rank-sum test) to haloperidol compared with other segregants.