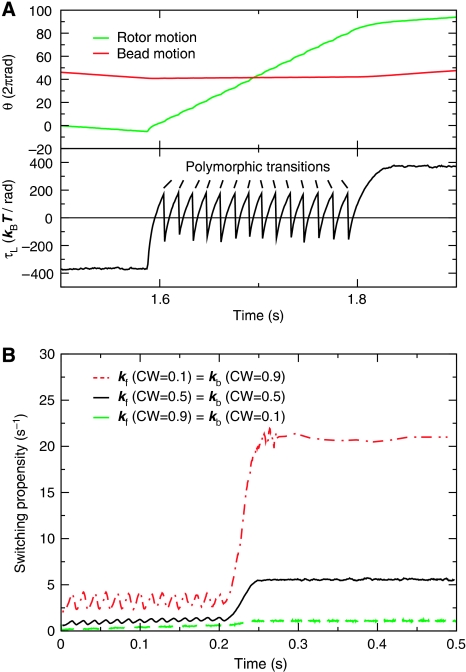
Figure 3.
The mechanism of switching. (A) Typical time traces for the load τL, rotor and bead position during a switching event, for CW bias=0.5. The arrows mark the polymorphic transitions of the flagellum (also see panel (D) of Box 1). Upon a polymorphic transition, the load instantly changes sign; the flagellum then pulls on the rotor in the forward rotation direction until the load crosses zero when the winding angle passes the value corresponding to the bottom of the potential well of the new conformational state (see panel (D) of Box 1); the flagellum then pulls on the rotor in the backward rotation direction until the next polymorphic transition occurs or the rotor reverses direction. (B) The switching propensity as a function of time after a switching event, for CW bias=0.1, 0.5, and 0.9.