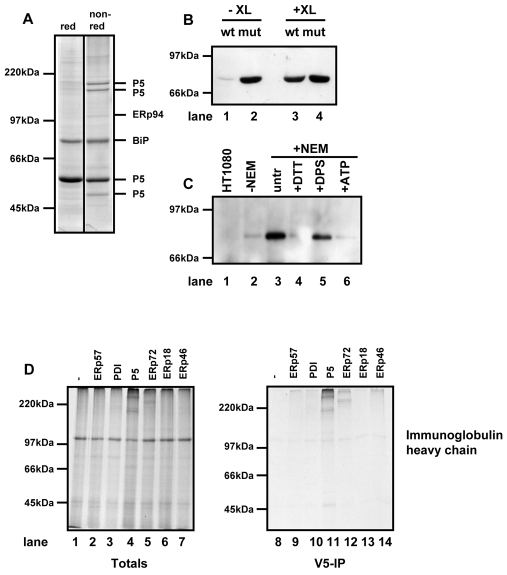
Fig. 3.
P5 forms a non-covalent interaction with BiP and associates with a BiP client protein. (A) HT1080 cells expressing substrate-trapping mutant of P5 was treated with NEM and lysed. Clarified lysates were immunoisolated with an anti-V5 antibody conjugated to agarose beads. Proteins were eluted by boiling in SDS and separated under reducing (red) or non-reducing (non-red) conditions. The protein bands were excised from the non-reducing gel and the indicated proteins identified by mass spectrometry. (B) HT1080 cells expressing either wild-type (wt) or the substrate-trapping mutant (mut) of P5 were either not treated (-XL) or treated (+XL) with a crosslinking agent. Cells were lysed and V5-tagged P5 immunoisolated using anti-V5 antibody immobilised on agarose beads. The immunoisolate was separated on by SDS-PAGE and western blotted with antibody against BiP. (C) Untransfected HT1080 cells (lane 1) or cells expressing the substrate-trapping mutant of P5 (lanes 2-6) were pretreated with 10 mM DTT (lane 4), 1 mM DPS (lane 5) or untreated (lanes 1, 2, 3, 6). Cells were either lysed in lysis buffer in the absence of NEM (lane 2) or lysed in the presence of NEM (lanes 1, 3-5) or in the presence of NEM and ATP (lane 6). V5-tagged P5 was immunoisolated with V5 agarose. The immunoisolate was separated by SDS-PAGE and western blotted with antibody against BiP. (D) Human immunoglobulin heavy chain was translated in the presence of SP cells prepared from either HT1080 cells (lanes 1 and 8) or cells expressing the substrate-trapping mutants of the PDI family members as indicated (lanes 2-7 and 9-14). Following translation for 2 hours, SP cells were isolated and products of translation were either separated by non-reducing SDS-PAGE immediately (totals; lanes 1-7) or following immunoisolation with V5-agarose (V5-IP; lanes 8-14). Radiolabelled proteins were visualised following autoradiography.