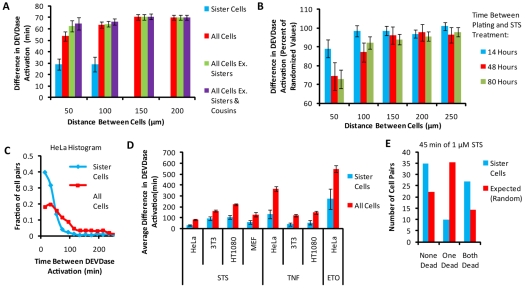
Fig. 3.
Distance between cells and initiation of apoptosis. (A) Analysis of the time difference of DEVDase activation as a function of distance between cells for sister cell cells (blue), between all cells (red), between all cells that are not sister cells (green), and between all cells that are not sister cells or cousin cells (purple) (n=562 cells in three fields). (B) Analysis of time difference of DEVDase activation as a function of distance for cells plated at various times prior to STS addition (ncells>385 for each time point). (C) Histogram of the difference in time of DEVDase activation between HeLa sister cells, and between randomly paired cells (n=265 pairs). (D) Average difference in DEVDase activation between sister cells (blue), and randomly paired cells (red) for HeLa, NIH3T3 and HT1080 cells treated with 2 μM STS, 250 ng/μl TNFα + 5 μg/ml CHX, or 50 μM ETO. Differences between sister and random distributions are significant for all cell types (STS: HeLa, P=6.2×10–34; 3T3, P=0.0011; HT1080, P=2.1×10–10; MEF, P=9.9×10–4. TNFα+CHX: HeLa, P=1.4×10–16; 3T3, P=4.7×10–14; HT1080, P=5.8×10–10. ETO: HeLa, P=1.2×10–11. For MEFs, npairs=21; for all other cells: npairs is between 54-106 pairs for different conditions). (E) HeLa cells treated with 1 μM STS for 45 minutes. In blue are counts of sister cell pairs where both cells die, only one cell dies and where both survive. In red is the expected value of the counts if there were no apoptosis similarity between sister cells, and given that 44% of all cells underwent apoptosis. All error bars represent the 95% confidence interval of the mean.