Fig. 1.
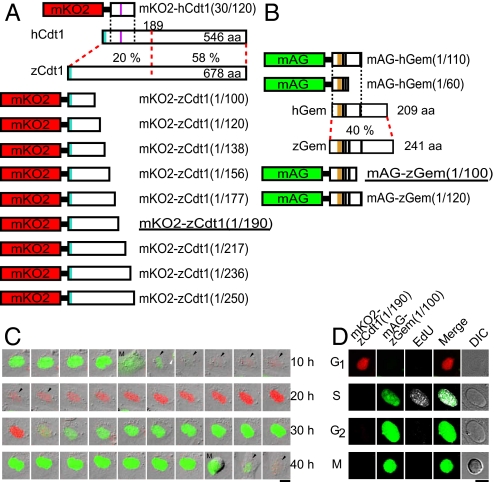
Development of fluorescent indicators for cell-cycle progression in fish cells (zFucci), and characterization of zFucci in transgenic fish (Cecyil) cells compared with Fucci in HeLa cells. (A) Structural domains of hCdt1 (human Cdt1) and zCdt1 (zebrafish Cdt1). Cyan box, PIP box or QXRVTDF motif (amino acids 3–9); violet box, Cy motif (amino acids 68–70). The N-terminal 189 aa of hCdt1 are sufficient for G1-specific accumulation of the protein (11). This regulatory region shows 20% sequence homology between hCdt1 and zCdt1. The other region, which contains the geminin and MCM6 binding domains, shows 58% homology between the two proteins. The G1 marker of the original Fucci, mKO2-hCdt1(30/120), is illustrated at the Top. Various constructs with concatenated mKO2 and deletion mutants of zCdt1 are shown at the Bottom. mKO2-zCdt1(1/190) is underlined. (B) Structural domains of hGem (human geminin) and zGem (zebrafish geminin). The S/G2/M markers of the original Fucci, mAG-hGem(1/110) and mAG-hGem(1/60), are illustrated at the Top. Two constructs with concatenated mAG and deletion mutants of hGem for labeling nuclei in S, G2, and M phases. mAG-zGem(1/100) is underlined. Orange box, D (destruction) box; black box, NLS (nuclear localization signal). (C) Cell-cycle-dependent changes in fluorescence of zFucci (mKO2-zCdt1(1/190) and mAG-zGem(1/100)) in Cecyil cells. Arrows indicate cells that were tracked. (Scale bar, 10 μm.) M, M phase. (D) Typical fluorescence images of Cecyil cells expressing zFucci (mKO2-zCdt1(1/190) and mAG-zGem(1/100)) and fluorescence from incorporated EdU (white) at G1, S, G2, and M phases. (Scale bar, 10 μm.)