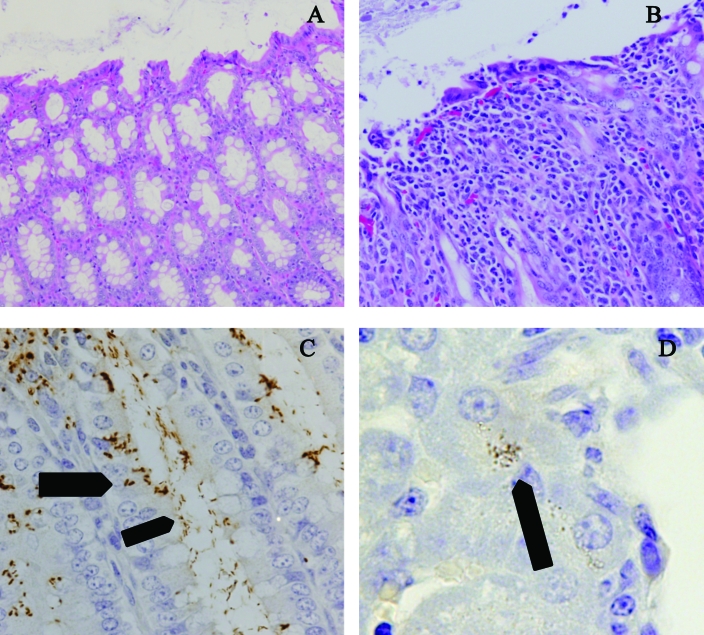
Figure 3.
Histopathology and immunohistochemistry of C. jejuni. (A) Colon of a control ferret, showing abundance of goblet cells, the columnar epithelium, and the distance between colonic crypts. Hematoxylin and eosin; magnification, ×20. (B) Colon of an infected ferret on day 3, showing the lack of goblet cells, attenuation and loss of epithelium, and separation of the colonic crypts by numerous inflammatory cells. Hematoxylin and eosin; magnification, ×20. (C) Colon of an infected ferret on day 3, showing presence of Campylobacter along the luminal surface(narrow arrow) as well as within or between enterocytes (wide arrow) by using immunohistochemistry for antiCampylobacter antibodies and hematoxylin counterstain. Magnification, ×40. (D) Liver of an infected ferret on day 1, showing Campylobacter within hepatocytes (arrow) by using immunohistochemistry for antiCampylobacter antibodies and hematoxylin counterstain (oil immersion). Magnification, ×100.