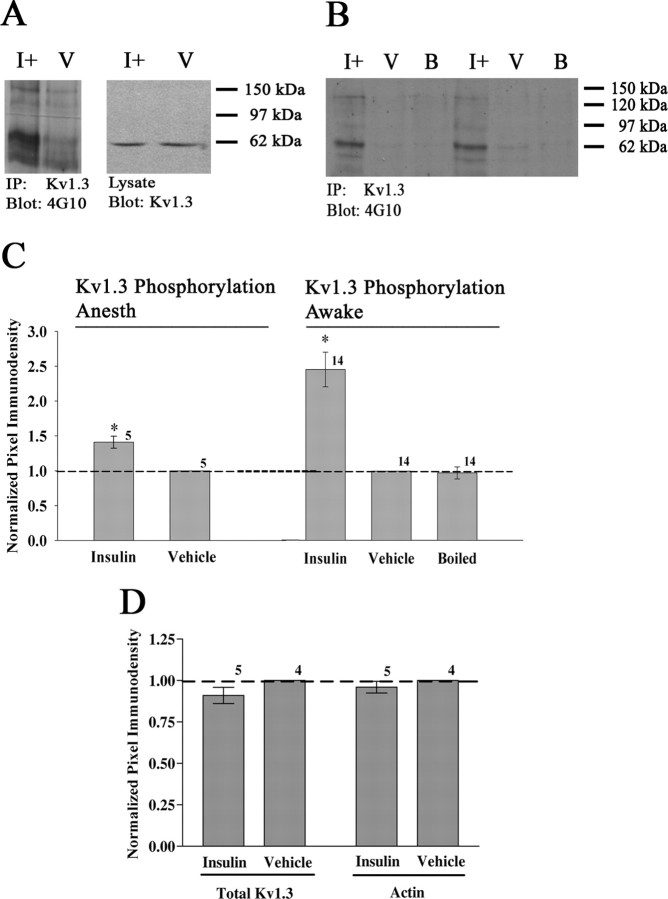
Figure 1.
Intranasal insulin evokes Kv1.3 tyrosine phosphorylation in anesthetized and awake animals. Representative Western blots and quantitative scanning densitometry summary histograms of Kv1.3 tyrosine phosphorylation under anesthetized (Kv1.3 Phosphorylation Anesth) (A, C) or awake (Kv1.3 Phosphorylation Awake) (B, C) states. Under both conditions, mice were intranasally administered insulin (I+), PBS vehicle (V), or boiled insulin (B) as indicated. Details of delivery and animal handling can be found in the methods. OBs were harvested, and Kv1.3 channel was immunoprecipitated from clarified OB lysates (IP: Kv1.3), separated via SDS-PAGE, and probed with anti-phosphotyrosine (blot: 4G10). OB lysates (lysate) were run in tandem with immunoprecipitated samples to demonstrate equal Kv1.3 expression and input (blot Kv1.3). C, Summary bar graph is the mean (±SEM) pixel density of the phosphorylated Kv1.3 band as normalized to the vehicle (dashed line, ratio of 1.0). D, Summary bar graph is the mean (±SEM) pixel density of two controls, total Kv1.3 channel (input) or actin as quantified from the lysates and similarly normalized to the vehicle. *Significantly different from vehicle by Student's t test, α = 0.05, arc-sin transformation for percentage data. Sample sizes are as indicated.